Arm rotated medially with supination - the ARMS variant: description of its surgical correction
- PMID: 19291305
- PMCID: PMC2664782
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2474-10-32
Arm rotated medially with supination - the ARMS variant: description of its surgical correction
Abstract
Background: Patients who have suffered obstetric brachial plexus injury (OBPI) have a high incidence of musculoskeletal complications stemming from the initial nerve injury. The presence of muscle imbalances and contractures leads to typical bony changes affecting the shoulder, including the SHEAR (Scapular Hypoplasia, Elevation and Rotation) deformity. The SHEAR deformity commonly occurs in conjunction with Medial Rotation Contracture (MRC) of the arm. OBPI also causes muscle imbalances at the level of the forearm, that lead to a fixed supination deformity (SD) in a small number of patients. Both MRC and SD will cause severe functional limitations without surgical intervention.
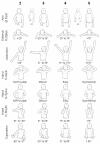
Methods: Fourteen OBPI patients were diagnosed with MRC of the shoulder and SD of the forearm along with SHEAR deformity during a 16 month study period, with eight patients available to long-term follow-up (age range 2.2 - 18 years). Surgical correction of the MRC was performed as a triangle tilt or humeral osteotomy depending on the age of the child, after which, the patients were treated with a radial osteotomy to correct the fixed supination deformity. Function was assessed using the modified Mallet scale, examination of apparent supination and appearance of the extremity at rest.
Results: Significant functional improvements were observed in patients with surgical reconstruction. Mallet score increased by an average of 5.2 (p < 0.05). Overall forearm position was not significantly changed from an average of 5 degrees to an average of 34 degrees maximum apparent supination after both shoulder rotation and forearm rotation corrective surgeries.
Conclusion: The simultaneous presence of two opposing deformities in the same limb will visually offset each other at the level of the wrist and hand, giving the false impression of neutral positioning of the limb. In reality, the neutral-appearing position of the hand indicates a fixed supination posture of the forearm in the face of a medial rotation contracture of the shoulder. Both of these deformities require surgical attention, and the presence of concurrent MRC and SD should be monitored for in OBPI patients.
Figures




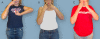

References
-
- Birch R. Medial rotation contracture and posterior dislocation of the shoulder. In: Gilbert A, editor. Brachial plexus injuries. First. London: Martin Dunitz, Ltd; 2001. pp. 249–259.
-
- Nath RK, Melcher SE, Paizi M. Surgical correction of unsuccessful derotational humeral osteotomy in obstetric brachial plexus palsy: Evidence of the significance of scapular deformity in the pathophysiology of the medial rotation contracture. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 2006;1:9. doi: 10.1186/1749-7221-1-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birch R, Bonney G, Wynn Parry CB. Birth lesions of the brachial plexus. In: Birch R, Bonney G, Wynn Parry CB, editor. Surgical disorders of the peripheral nerves. New York, NY: Churchill Livingstone; 1998. pp. 209–233.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

