Alpha2-adrenergic impact on hypothalamic magnocellular oxytocinergic neurons in long evans and brattleboro rats: effects of agonist and antagonists
- PMID: 19291390
- PMCID: PMC11506120
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-009-9388-0
Alpha2-adrenergic impact on hypothalamic magnocellular oxytocinergic neurons in long evans and brattleboro rats: effects of agonist and antagonists
Abstract
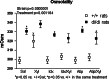
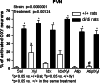
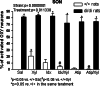
We have previously demonstrated that alpha2-adrenoceptors regulate hypothalamic magnocellular oxytocinergic (OXY) neurons in Sprague Dawley rats. Here we investigated whether activation/inhibition of alpha2-adrenoceptors may similarly trigger/downregulate the activity of OXY neurons in control Long Evans (+/+) and permanently osmotically stressed Brattleboro (di/di) rats. The effect of alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist, xylazine (XYL) and alpha2-adrenoceptor antagonists, atipamezole (ATIP), and idazoxan (IDX) were evaluated in the supraoptic (SON) and paraventricular (PVN) hypothalamic nuclei. Saline (SAL, 0.1 ml/100 g), XYL (10 mg/kg), ATIP, (1 mg/kg), and IDX (10 mg/kg) and IDX or ATIP followed by XYL were applied intraperitoneally. Rats were sacrificed 90 min later and Fos/OXY co-labelings analyzed in microscope. In control +/+ rats no or few Fos/OXY co-labelings occurred in SON and PVN. XYL significantly increased Fos incidence in OXY neurons in both nuclei. ATIP significantly suppressed the effect of XYL in both nuclei and IDX only in SON. In di/di controls 81% of OXY neurons in SON and 44% in PVN revealed Fos presence and XYL did not further elevate Fos number in SON OXY neurons and slightly increased Fos number in PVN. ATIP or IDX only partially reduced Fos in SAL or XYL treated di/di rats. Our data indicate that: (1) XYL stimulation is not effective in di/di rats because of sustained upregulation of OXY neurons activity and (2) neither ATIP nor IDX reduced significantly the OXY activity in control di/di rats. These findings suggest that alpha2-adrenoceptors have only a limited impact in maintaining OXY cells activity upregulation in PVN and SON of di/di rats.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

