Scratching behavior and Fos expression in superficial dorsal horn elicited by protease-activated receptor agonists and other itch mediators in mice
- PMID: 19293390
- PMCID: PMC2683773
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.109.152256
Scratching behavior and Fos expression in superficial dorsal horn elicited by protease-activated receptor agonists and other itch mediators in mice
Abstract
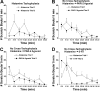
Protease-activated receptor (PAR)-2 and PAR-4 are implicated in nonhistaminergic itch. We investigated dose dependence, tachyphylaxis, and cross-tachyphylaxis of itch-associated scratching elicited by intradermal injections of PAR-2 and PAR-4 agonists, serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT), and histamine in ICR mice, as well as mu-opioid modulation of PAR-2 agonist-evoked scratching. Each agent elicited dose-related increases in scratch bouts. Scratching elicited by the PAR-4 agonist and histamine both exhibited significant tachyphylaxis but no cross-tachyphylaxis with each other. Scratching evoked by 5-HT did not exhibit significant tachyphylaxis but did exhibit significant cross-tachyphylaxis to scratching evoked by the PAR-2 and PAR-4 agonists and histamine. Naltrexone and high-dose morphine (10 mg/kg) attenuated PAR-2 agonist-evoked scratching, whereas lower dose morphine (1 mg/kg) had no effect. High-dose morphine also significantly increased circling behavior, which may have interfered with scratching. The PAR-2 agonist and 5-HT produced overlapping distributions of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the superficial dorsal horn. These results indicate that PAR-2 and PAR-4 agonists, histamine, and 5-HT elicit itch-related scratching and activate superficial dorsal horn neurons that may participate in scratch reflex and ascending itch signaling pathways.
Figures
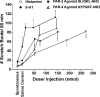



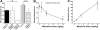
 ), or
naltrexone (1 mg/kg; □), respectively. *, p < 0.01,
significant difference between saline and naltrexone groups (n =
5–6/group). Bars to right show scratching elicited by intradermal
capsaicin (10 μg/10 μl;
), or
naltrexone (1 mg/kg; □), respectively. *, p < 0.01,
significant difference between saline and naltrexone groups (n =
5–6/group). Bars to right show scratching elicited by intradermal
capsaicin (10 μg/10 μl;  )
and lack of significant effect of naltrexone
(
)
and lack of significant effect of naltrexone
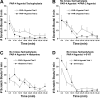
( ). B, graph plots total number
of scratch bouts/45 min elicited by the PAR-2 agonist SLIGRL-NH2
versus dose of morphine. The number of scratch bouts at 1- and 3-mg/kg doses
of morphine was not significantly different from vehicle but was significantly
lower (*, p < 0.05) at the highest morphine dose (10 mg/kg). C,
graph plots mean number of rotations (circling)/45 min versus dose of
morphine. *, p < 0.05 for all, significantly different from 0-,
1-, and 3-mg/kg doses.
). B, graph plots total number
of scratch bouts/45 min elicited by the PAR-2 agonist SLIGRL-NH2
versus dose of morphine. The number of scratch bouts at 1- and 3-mg/kg doses
of morphine was not significantly different from vehicle but was significantly
lower (*, p < 0.05) at the highest morphine dose (10 mg/kg). C,
graph plots mean number of rotations (circling)/45 min versus dose of
morphine. *, p < 0.05 for all, significantly different from 0-,
1-, and 3-mg/kg doses.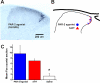
References
-
- Andrew D and Craig AD (2001) Spinothalamic lamina I neurons selectively sensitive to histamine: a central neural pathway for itch. Nat Neurosci 4 72-77. - PubMed
-
- Cottrell GS, Amadesi S, Schmidlin F, and Bunnett N (2003) Protease-activated receptor 2: activation, signalling and function. Biochem Soc Trans 31 1191-1197. - PubMed
-
- Cuellar JM, Jinks SL, Simons CT, and Carstens E (2003) Deletion of the preprotachykinin A gene in mice does not reduce scratching behavior elicited by intradermal serotonin. Neurosci Lett 339 72-76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

