Force- and length-dependent catastrophe activities explain interphase microtubule organization in fission yeast
- PMID: 19293826
- PMCID: PMC2671915
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2008.76
Force- and length-dependent catastrophe activities explain interphase microtubule organization in fission yeast
Abstract
The cytoskeleton is essential for the maintenance of cell morphology in eukaryotes. In fission yeast, for example, polarized growth sites are organized by actin, whereas microtubules (MTs) acting upstream control where growth occurs. Growth is limited to the cell poles when MTs undergo catastrophes there and not elsewhere on the cortex. Here, we report that the modulation of MT dynamics by forces as observed in vitro can quantitatively explain the localization of MT catastrophes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. However, we found that it is necessary to add length-dependent catastrophe rates to make the model fully consistent with other previously measured traits of MTs. We explain the measured statistical distribution of MT-cortex contact times and re-examine the curling behavior of MTs in unbranched straight tea1Delta cells. Importantly, the model demonstrates that MTs together with associated proteins such as depolymerizing kinesins are, in principle, sufficient to mark the cell poles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

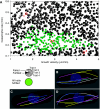
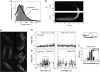
Comment in
-
Toward a comprehensive and quantitative understanding of intracellular microtubule organization.Mol Syst Biol. 2009;5:251. doi: 10.1038/msb.2009.7. Epub 2009 Mar 17. Mol Syst Biol. 2009. PMID: 19293831 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Brunner D, Nurse P (2000) CLIP170-like tip1p spatially organizes microtubular dynamics in fission yeast. Cell 102: 695–704 - PubMed
-
- Carazo-Salas RE, Nurse P (2006) Self-organization of interphase microtubule arrays in fission yeast. Nat Cell Biol 8: 1102–1107 - PubMed
-
- Csikasz-Nagy A, Gyorffy B, Alt W, Tyson JJ, Novak B (2008) Spatial controls for growth zone formation during the fission yeast cell cycle. Yeast 25: 59–69 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

