Detection of partial-thickness supraspinatus tendon tears: is a single direct MR arthrography series in ABER position as accurate as conventional MR arthrography?
- PMID: 19294377
- PMCID: PMC2733185
- DOI: 10.1007/s00256-009-0680-3
Detection of partial-thickness supraspinatus tendon tears: is a single direct MR arthrography series in ABER position as accurate as conventional MR arthrography?
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to retrospectively evaluate sensitivity and specificity of a single magnetic resonance (MR) arthrography series in abduction external rotation (ABER) position compared with conventional MR arthrography for detection of supraspinatus tendon tears, with arthroscopy as gold standard, and to assess interobserver variability.
Materials and methods: Institutional review board approval was obtained; informed consent was waived. MR arthrograms of 250 patients (170 men and 80 women; mean age, 36 years) were retrospectively and independently evaluated by three observers. Oblique coronal T1-weighted fat-suppressed images, proton density, and T2-weighted images and axial T1-weighted images and oblique sagittal T1-weighted fat-suppressed images were analyzed to detect supraspinatus tendon tears. Separately, a single T1-weighted fat-suppressed oblique axial series in ABER position was evaluated. Both protocols were scored randomly without knowledge of patients' clinical history and arthroscopy results. Tears were subclassified, based on articular surface integrity and extension (Lee classification). Interobserver agreement was assessed by kappa statistics for all patients. Ninety-two of 250 patients underwent arthroscopy; sensitivity and specificity of ABER and conventional MR arthrography were calculated and compared using paired McNemar test.
Results: Weighted kappa values of ABER and conventional MR arthrography were 0.48-0.65 and 0.60-0.67, respectively. According to arthroscopy, 69 of 92 patients had an intact cuff, and 23 patients had a cuff tear (16 partial thickness and seven full thickness). There were no statistically significant differences between ABER and conventional MR arthrography regarding sensitivity (48-61% and 52-70%, respectively) and specificity (80-94% and 91-95%).
Conclusion: Sensitivity and specificity of a single T1-weighted series in ABER position and conventional MR arthrography are comparable for assessment of rotator cuff tears.
Figures
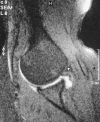
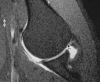
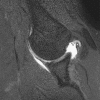
Comment in
-
[Isolated direct MR arthrography in ABER position or conventional MR arthrography for identification of partial ruptures of the supraspinatus tendon].Radiologe. 2011 Jan;51(1):6-7. doi: 10.1007/s00117-010-2097-3. Radiologe. 2011. PMID: 21174073 German. No abstract available.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1136/ard.54.12.959', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.54.12.959'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1010060', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1010060/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '8546527', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/8546527/'}]}
- van der Windt DA, Koes BW, de Jong BA, Bouter LM. Shoulder disorders in general practice: incidence, patient characteristics, and management. Ann Rheum Dis. 1995; 54(12): 959–964. - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1097/00000658-193101000-00043', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1097/00000658-193101000-00043'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC1398744', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC1398744/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '17866481', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17866481/'}]}
- Codman EA, Akerson ID. The pathology associated with rupture of the supraspinatus tendon. Ann Surg. 1931; 93: 348. - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2323148', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2323148/'}]}
- Ogata S, Uhthoff HK. Acromial enthesopathy and rotator cuff tear: a radiologic and histologic postmortem investigation of the coracoacromial arch. Clin Orthop. 1990; 254: 39–48. - PubMed
-
- None
- Bigliani LU, Morrison DS, April EW. The morphology of the acromion and the rotator cuff: importance. Orthop Trans. 1986; 10: 228.
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1016/S0030-5898(05)70261-3', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1016/s0030-5898(05)70261-3'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9024428', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9024428/'}]}
- Soslowsky LJ, Carpenter JE, Bucchieri JS, Flatow EL. Biomechanics of the rotator cuff. Orthop Clin North Am. 1997; 28: 17–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

