Preparation and evaluation of miconazole nitrate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for topical delivery
- PMID: 19294517
- PMCID: PMC2663689
- DOI: 10.1208/s12249-009-9199-0
Preparation and evaluation of miconazole nitrate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for topical delivery
Abstract
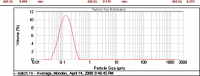
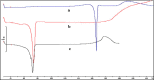
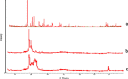
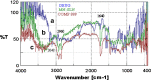
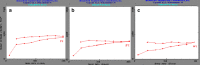
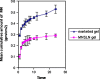
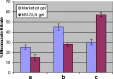
The purpose of this study was to prepare miconazole nitrate (MN) loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (MN-SLN) effective for topical delivery of miconazole nitrate. Compritol 888 ATO as lipid, propylene glycol (PG) to increase drug solubility in lipid, tween 80, and glyceryl monostearate were used as the surfactants to stabilize SLN dispersion in the SLN preparation using hot homogenization method. SLN dispersions exhibited average size between 244 and 766 nm. All the dispersions had high entrapment efficiency ranging from 80% to 100%. The MN-SLN dispersion which showed good stability for a period of 1 month was selected. This MN-SLN was characterized for particle size, entrapment efficiency, and X-ray diffraction. The penetration of miconazole nitrate from the gel formulated using selected MN-SLN dispersion as into cadaver skins was evaluated ex-vivo using franz diffusion cell. The results of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) showed that MN was dispersed in SLN in an amorphous state. The MN-SLN formulations could significantly increase the accumulative uptake of MN in skin over the marketed gel and showed a significantly enhanced skin targeting effect. These results indicate that the studied MN-SLN formulation with skin targeting may be a promising carrier for topical delivery of miconazole nitrate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Propylene glycol liposomes as a topical delivery system for miconazole nitrate: comparison with conventional liposomes.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012 Jun;13(2):723-31. doi: 10.1208/s12249-012-9783-6. Epub 2012 May 8. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012. PMID: 22566173 Free PMC article.
-
Halobetasol propionate-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for skin targeting by topical delivery.J Liposome Res. 2014 Jun;24(2):113-23. doi: 10.3109/08982104.2013.843192. Epub 2013 Oct 17. J Liposome Res. 2014. PMID: 24131382
-
Isotretinoin-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles with skin targeting for topical delivery.Int J Pharm. 2007 Jan 10;328(2):191-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2006.08.007. Epub 2006 Aug 15. Int J Pharm. 2007. PMID: 16978810
-
Nano-Sized Technologies for Miconazole Skin Delivery.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016;17(6):524-31. doi: 10.2174/1389201017666160301102459. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26927217 Review.
-
Mechanisms of solid lipid nanoparticles-triggered signaling pathways in eukaryotic cells.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022 Dec;220:112863. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2022.112863. Epub 2022 Sep 21. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022. PMID: 36272282 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanostructured Lipid Carriers (NLC)-Based Gel for the Topical Delivery of Aceclofenac: Preparation, Characterization, and In Vivo Evaluation.Sci Pharm. 2012 Jul-Sep;80(3):749-64. doi: 10.3797/scipharm.1202-12. Epub 2012 Jun 18. Sci Pharm. 2012. PMID: 23008819 Free PMC article.
-
Current applications and prospects of nanoparticles for antifungal drug delivery.EXCLI J. 2021 Mar 8;20:562-584. doi: 10.17179/excli2020-3068. eCollection 2021. EXCLI J. 2021. PMID: 33883983 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Niosomal gel of lornoxicam for topical delivery: in vitro assessment and pharmacodynamic activity.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2013 Sep;14(3):1072-82. doi: 10.1208/s12249-013-9986-5. Epub 2013 Jul 2. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2013. PMID: 23818079 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged Skin Retention of Luliconazole from SLNs Based Topical Gel Formulation Contributing to Ameliorated Antifungal Activity.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Oct 1;25(7):229. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02945-0. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 39354184
-
Prospect of nanomaterials as antimicrobial and antiviral regimen.AIMS Microbiol. 2023 May 10;9(3):444-466. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2023024. eCollection 2023. AIMS Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37649798 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

