Inhibition of mammary tumor growth and metastases to bone and liver by dietary grape polyphenols
- PMID: 19294520
- PMCID: PMC2898569
- DOI: 10.1007/s10585-009-9250-2
Inhibition of mammary tumor growth and metastases to bone and liver by dietary grape polyphenols
Abstract
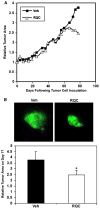
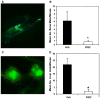
The cancer preventive properties of grape products such as red wine have been attributed to polyphenols enriched in red wine. However, much of the studies on cancer preventive mechanisms of grape polyphenols have been conducted with individual compounds at concentrations too high to be achieved via dietary consumption. We recently reported that combined grape polyphenols at physiologically relevant concentrations are more effective than individual compounds at inhibition of ERalpha(-), ERbeta(+) MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and primary mammary tumor growth (Schlachterman et al., Transl Oncol 1:19-27, 2008). Herein, we show that combined grape polyphenols induce apoptosis and are more effective than individual resveratrol, quercetin, or catechin at inhibition of cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and cell migration in the highly metastatic ER (-) MDA-MB-435 cell line. The combined effect of dietary grape polyphenols (5 mg/kg each resveratrol, quercetin, and catechin) was tested on progression of mammary tumors in nude mice created from green fluorescent protein-tagged MDA-MB-435 bone metastatic variant. Fluorescence image analysis of primary tumor growth demonstrated a statistically significant decrease in tumor area by dietary grape polyphenols. Molecular analysis of excised tumors demonstrated that reduced mammary tumor growth may be due to upregulation of FOXO1 (forkhead box O1) and NFKBIA (IkappaBalpha), thus activating apoptosis and potentially inhibiting NfkappaB (nuclear factor kappaB) activity. Image analysis of distant organs for metastases demonstrated that grape polyphenols reduced metastasis especially to liver and bone. Overall, these results indicate that combined dietary grape polyphenols are effective at inhibition of mammary tumor growth and site-specific metastasis.
Figures
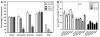



References
-
- Rastelli F, Crispino S. Factors predictive of response to hormone therapy in breast cancer. Tumori. 2008;94:370–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R03 CA109913/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007583/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM061838/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- SC3 GM111171/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- G11 HD052352/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- G12 RR003051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 2G12RR003035/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G12-RR03051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 5R25GM061838-08/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- G11HD052352/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- S06 GM050695/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- G12 RR003035/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- G12 MD007600/MD/NIMHD NIH HHS/United States
- S06GM050695/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

