ATP, P2 receptors and the renal microcirculation
- PMID: 19294530
- PMCID: PMC2776135
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-009-9147-1
ATP, P2 receptors and the renal microcirculation
Abstract
Purinoceptors are rapidly becoming recognised as important regulators of tissue and organ function. Renal expression of P2 receptors is broad and diverse, as reflected by the fact that P2 receptors have been identified in virtually every major tubular/vascular element. While P2 receptor expression by these renal structures is recognised, the physiological functions that they serve remains to be clarified. Renal vascular P2 receptor expression is complex and poorly understood. Evidence suggests that different complements of P2 receptors are expressed by individual renal vascular segments. This unique distribution has given rise to the postulate that P2 receptors are important for renal vascular function, including regulation of preglomerular resistance and autoregulatory behaviour. More recent studies have also uncovered evidence that hypertension reduces renal vascular reactivity to P2 receptor stimulation in concert with compromised autoregulatory capability. This review will consolidate findings related to the role of P2 receptors in regulating renal microvascular function and will present areas of controversy related to the respective roles of ATP and adenosine in autoregulatory resistance adjustments.
Figures

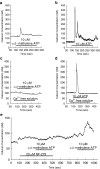
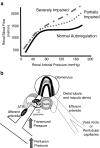
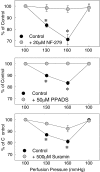
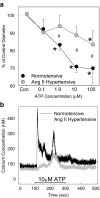
References
-
- Bailey MA, Hillman KA, Unwin RJ (2000) P2 receptors in the kidney. J Auton Nerv Syst 81:264–270 - PubMed
-
- Bailey MA, Imbert-Teboul M, Turner C, Marsy S, Srai K, Burnstock G, Unwin RJ (2000) Axial distribution and characterization of basolateral P2Y receptors along the rat renal tubule. Kidney Int 58:1893–1901 - PubMed
-
- Bailey MA, Turner CM, Hus-Citharel A, Marchetti J, Imbert-Teboul M, Milner P, Burnstock G, Unwin R (2004) P2Y receptors present in the native and isolated rat glomerulus. Nephron Physiol 96:79–90 - PubMed
-
- Chan CM, Unwin RJ, Bardini M, Oglesby IB, Ford APDW, Townsend-Nicholson A, Burnstock G (1998) Localization of the P2X1 purinoceptors by autoradiography and immunohistochemistry in the rat kidney. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 274:F799–F804 - PubMed
-
- Chan CM, Unwin RJ, Burnstock G (1998) Potential functional roles of extracellular ATP in kidney and urinary tract. Exp Nephrol 6:200–207 - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

