Epithelial-derived brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for gustatory neuron targeting during a critical developmental period
- PMID: 19295142
- PMCID: PMC2683425
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3970-08.2009
Epithelial-derived brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for gustatory neuron targeting during a critical developmental period
Abstract
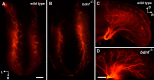
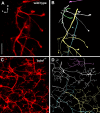
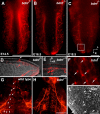
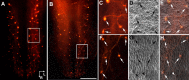
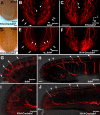
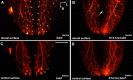
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is expressed in epithelial targets of gustatory neurons (i.e., fungiform papillae) before their innervation, and BDNF overexpression in nontaste regions of the tongue misdirects gustatory axons to these sites, suggesting that BDNF is necessary for gustatory axons to locate and innervate their correct targets during development. To test this hypothesis, we examined the targeting of taste neurons in BDNF-null mice (bdnf(-/-)). Analysis of bdnf(-/-) mice using a combination of DiI labeling and electron microscopy revealed that taste regions were not innervated by gustatory axons. Instead, branching was increased and many nontaste regions were innervated. The increased branching by gustatory axons in these animals was facilitated by neurotrophin 4 (NT4), because branching was virtually eliminated in bdnf(-/-)/nt4(-/-) mice. No abnormalities in gustatory innervation patterns and targeting were observed in nt4(-/-) mice. Conditional removal of BDNF selectively in epithelial cells disrupted targeting at the tongue tip, where gene recombination removed bdnf by embryonic day 13.5 (E13.5). However, innervation patterns were normal in the midregion and caudal portions of the tongue, where gene recombination did not occur until E14.5. These findings demonstrate that BDNF derived from gustatory epithelia is required for gustatory axons to correctly locate and innervate fungiform papillae. In addition, they show that BDNF-mediated targeting is restricted to a critical period of development, on or before E13.5.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The neurotrophin receptor p75 regulates gustatory axon branching and promotes innervation of the tongue during development.Neural Dev. 2014 Jun 24;9:15. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-9-15. Neural Dev. 2014. PMID: 24961238 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial overexpression of BDNF or NT4 disrupts targeting of taste neurons that innervate the anterior tongue.Dev Biol. 2001 Apr 15;232(2):508-21. doi: 10.1006/dbio.2001.0190. Dev Biol. 2001. PMID: 11401409
-
Epithelial overexpression of BDNF and NT4 produces distinct gustatory axon morphologies that disrupt initial targeting.Dev Biol. 2006 Apr 15;292(2):457-68. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.01.021. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16500639 Free PMC article.
-
Taste neurons have multiple inductive roles in mammalian gustatory development.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Nov 30;855:50-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb10545.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9929585 Review.
-
Building sensory receptors on the tongue.J Neurocytol. 2004 Dec;33(6):631-46. doi: 10.1007/s11068-005-3332-0. Epub 2005 Oct 11. J Neurocytol. 2004. PMID: 16217619 Review.
Cited by
-
Taste bud-derived BDNF maintains innervation of a subset of TrkB-expressing gustatory nerve fibers.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017 Jul;82:195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2017.06.001. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28600222 Free PMC article.
-
Epibranchial placode-derived neurons produce BDNF required for early sensory neuron development.Dev Dyn. 2011 Feb;240(2):309-23. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.22527. Epub 2011 Jan 5. Dev Dyn. 2011. PMID: 21246648 Free PMC article.
-
Mice deficient in brain-derived neurotrophic factor have altered development of gastric vagal sensory innervation.J Comp Neurol. 2010 Aug 1;518(15):2934-51. doi: 10.1002/cne.22372. J Comp Neurol. 2010. PMID: 20533354 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor attracts geniculate ganglion neurites during embryonic targeting.Dev Neurosci. 2010 Aug;32(3):184-96. doi: 10.1159/000313902. Epub 2010 Jul 20. Dev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20639634 Free PMC article.
-
The neurotrophin receptor p75 regulates gustatory axon branching and promotes innervation of the tongue during development.Neural Dev. 2014 Jun 24;9:15. doi: 10.1186/1749-8104-9-15. Neural Dev. 2014. PMID: 24961238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conover JC, Erickson JT, Katz DM, Bianchi LM, Poueymirou WT, McClain J, Pan L, Helgren M, Ip NY, Boland P, Friedman B, Wiegand S, Vejsada R, Kato AC, Dechiara TM, Yancopoulos GD. Neuronal deficits, not involving motor neurons, in mice lacking BDNF and/or NT4. Nature. 1995;375:235–238. - PubMed
-
- Dassule HR, Lewis P, Bei M, Maas R, McMahon AP. Sonic hedgehog regulates growth and morphogenesis of the tooth. Development. 2000;127:4775–4785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
