Inflammation triggers synaptic alteration and degeneration in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- PMID: 19295150
- PMCID: PMC6665268
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5804-08.2009
Inflammation triggers synaptic alteration and degeneration in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
Abstract
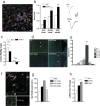
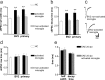
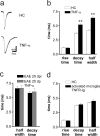
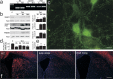
Neurodegeneration is the irremediable pathological event occurring during chronic inflammatory diseases of the CNS. Here we show that, in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), a mouse model of multiple sclerosis, inflammation is capable in enhancing glutamate transmission in the striatum and in promoting synaptic degeneration and dendritic spine loss. These alterations occur early in the disease course, are independent of demyelination, and are strongly associated with massive release of tumor necrosis factor-alpha from activated microglia. CNS invasion by myelin-specific blood-borne immune cells is the triggering event, and the downregulation of the early gene Arc/Arg3.1, leading to the abnormal expression and phosphorylation of AMPA receptors, represents a culminating step in this cascade of neurodegenerative events. Accordingly, EAE-induced synaptopathy subsided during pharmacological blockade of AMPA receptors. Our data establish a link between neuroinflammation and synaptic degeneration and calls for early neuroprotective therapies in chronic inflammatory diseases of the CNS.
Figures

References
-
- Bakshi R, Benedict RH, Bermel RA, Caruthers SD, Puli SR, Tjoa CW, Fabiano AJ, Jacobs L. T2 hypointensity in the deep gray matter of patients with multiple sclerosis: a quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study. Arch Neurol. 2002;59:62–68. - PubMed
-
- Barres BA. The mystery and magic of glia: a perspective on their roles in health and disease. Neuron. 2008;60:430–440. - PubMed
-
- Beattie EC, Stellwagen D, Morishita W, Bresnahan JC, Ha BK, Von Zastrow M, Beattie MS, Malenka RC. Control of synaptic strength by glial TNFalpha. Science. 2002;295:2282–2285. - PubMed
-
- Bermel RA, Innus MD, Tjoa CW, Bakshi R. Selective caudate atrophy in multiple sclerosis: a 3D MRI parcellation study. Neuroreport. 2003;14:335–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
