Reduced thin filament length in nebulin-knockout skeletal muscle alters isometric contractile properties
- PMID: 19295172
- PMCID: PMC2681381
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00503.2008
Reduced thin filament length in nebulin-knockout skeletal muscle alters isometric contractile properties
Abstract
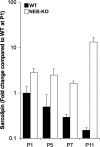
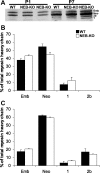
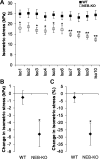
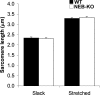
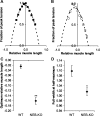
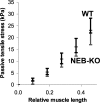
Nebulin (NEB) is a large, rod-like protein believed to dictate actin thin filament length in skeletal muscle. NEB gene defects are associated with congenital nemaline myopathy. The functional role of NEB was investigated in gastrocnemius muscles from neonatal wild-type (WT) and NEB knockout (NEB-KO) mice, whose thin filaments have uniformly shorter lengths compared with WT mice. Isometric stress production in NEB-KO skeletal muscle was reduced by 27% compared with WT skeletal muscle on postnatal day 1 and by 92% on postnatal day 7, consistent with functionally severe myopathy. NEB-KO muscle was also more susceptible to a decline in stress production during a bout of 10 cyclic isometric tetani. Length-tension properties in NEB-KO muscle were altered in a manner consistent with reduced thin filament length, with length-tension curves from NEB-KO muscle demonstrating a 7.4% narrower functional range and an optimal length reduced by 0.13 muscle lengths. Expression patterns of myosin heavy chain isoforms and total myosin content did not account for the functional differences between WT and NEB-KO muscle. These data indicate that NEB is essential for active stress production, maintenance of functional integrity during cyclic activation, and length-tension properties consistent with a role in specifying normal thin filament length. Continued analysis of NEB's functional properties will strengthen the understanding of force transmission and thin filament length regulation in skeletal muscle and may provide insights into the molecular processes that give rise to nemaline myopathy.
Figures


References
-
- Agbulut O, Noirez P, Beaumont F, Butler-Browne G. Myosin heavy chain isoforms in postnatal muscle development of mice. Biol Cell 95: 399–406, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Bang ML, Gregorio C, Labeit S. Molecular dissection of the interaction of desmin with the C-terminal region of nebulin. J Struct Biol 137: 119–127, 2002. - PubMed
-
- Burkholder TJ, Fingado B, Baron S, Lieber RL. Relationship between muscle fiber types and sizes and muscle architectural properties in the mouse hindlimb. J Morphol 221: 177–190, 1994. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

