Activation of CaMKII in single dendritic spines during long-term potentiation
- PMID: 19295602
- PMCID: PMC2719773
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07842
Activation of CaMKII in single dendritic spines during long-term potentiation
Abstract
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II (CaMKII) plays a central part in long-term potentiation (LTP), which underlies some forms of learning and memory. Here we monitored the spatiotemporal dynamics of CaMKII activation in individual dendritic spines during LTP using two-photon fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy, in combination with two-photon glutamate uncaging. Induction of LTP and associated spine enlargement in single spines triggered transient ( approximately 1 min) CaMKII activation restricted to the stimulated spines. CaMKII in spines was specifically activated by NMDA receptors and L-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels, presumably by nanodomain Ca(2+) near the channels, in response to glutamate uncaging and depolarization, respectively. The high degree of compartmentalization and channel specificity of CaMKII signalling allow stimuli-specific spatiotemporal patterns of CaMKII signalling and may be important for synapse-specificity of synaptic plasticity.
Figures
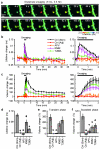
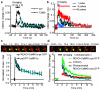
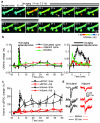
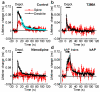
Comment in
-
Neuroscience: Secret of synapse specificity.Nature. 2009 Mar 19;458(7236):296-7. doi: 10.1038/458296a. Nature. 2009. PMID: 19295601 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rosenberg OS, et al. Oligomerization states of the association domain and the holoenyzme of Ca2+/CaM kinase II. Febs J. 2006;273:682–694. - PubMed
-
- Lisman JE, Zhabotinsky AM. A model of synaptic memory: a CaMKII/PP1 switch that potentiates transmission by organizing an AMPA receptor anchoring assembly. Neuron. 2001;31:191–201. - PubMed
-
- Merrill MA, Chen Y, Strack S, Hell JW. Activity-driven postsynaptic translocation of CaMKII. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005;26:645–653. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

