Cross-regulation of signaling by ITAM-associated receptors
- PMID: 19295630
- PMCID: PMC2753670
- DOI: 10.1038/ni.1706
Cross-regulation of signaling by ITAM-associated receptors
Abstract
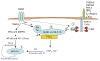
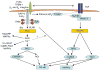
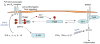
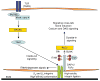
An important function of receptors that signal through immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) is to regulate signaling by heterologous receptors. This review describes mechanisms by which ITAM-associated receptors modulate signaling by Toll-like receptors (TLRs), tumor necrosis factor receptor family members and cytokine receptors that use the Jak-STAT signaling pathway, and the biological importance of this signal transduction cross-talk. ITAM-mediated cross-regulation can either augment or dampen signaling by other receptors. Conversely, TLRs and cytokines modulate ITAM-mediated signaling, by means including activation of beta2 integrins that are coupled to the ITAM-containing adaptors DAP12 and FcRgamma. Integration of ITAM signaling into signaling networks through cross-talk with other signal transduction pathways results in tight regulation and fine tuning of cellular responses to various extracellular stimuli and contributes to induction of specific activation and differentiation pathways.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ITAM-coupled receptors inhibit IFNAR signaling and alter macrophage responses to TLR4 and Listeria monocytogenes.J Immunol. 2012 Apr 1;188(7):3447-57. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102211. Epub 2012 Feb 24. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22368279 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk among Jak-STAT, Toll-like receptor, and ITAM-dependent pathways in macrophage activation.J Leukoc Biol. 2007 Aug;82(2):237-43. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1206763. Epub 2007 May 14. J Leukoc Biol. 2007. PMID: 17502339 Review.
-
Indirect inhibition of Toll-like receptor and type I interferon responses by ITAM-coupled receptors and integrins.Immunity. 2010 Apr 23;32(4):518-30. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2010.03.014. Epub 2010 Apr 1. Immunity. 2010. PMID: 20362473 Free PMC article.
-
Integrin signaling in neutrophils and macrophages uses adaptors containing immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs.Nat Immunol. 2006 Dec;7(12):1326-33. doi: 10.1038/ni1407. Epub 2006 Nov 5. Nat Immunol. 2006. PMID: 17086186 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of cytokine and heterologous receptor signaling pathways.Nat Immunol. 2009 Apr;10(4):333-9. doi: 10.1038/ni.1713. Epub 2009 Mar 19. Nat Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19295629 Review.
Cited by
-
Receptor cross-talk spatially restricts p-ERK during TLR4 stimulation of autoreactive B cells.J Immunol. 2012 Oct 15;189(8):3859-68. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1200940. Epub 2012 Sep 14. J Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22984080 Free PMC article.
-
Fine tuning inflammation at the front door: macrophage complement receptor 3-mediates phagocytosis and immune suppression for Francisella tularensis.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Jan;9(1):e1003114. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003114. Epub 2013 Jan 24. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 23359218 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-23 Regulates Inflammatory Osteoclastogenesis via Activation of CLEC5A(+) Osteoclast Precursors.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023 Aug;75(8):1477-1489. doi: 10.1002/art.42478. Epub 2023 Jun 6. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36787107 Free PMC article.
-
An Ancient BCR-like Signaling Promotes ICP Production and Hemocyte Phagocytosis in Oyster.iScience. 2020 Feb 21;23(2):100834. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.100834. Epub 2020 Jan 11. iScience. 2020. PMID: 31982779 Free PMC article.
-
RBP-J imposes a requirement for ITAM-mediated costimulation of osteoclastogenesis.J Clin Invest. 2014 Nov;124(11):5057-73. doi: 10.1172/JCI71882. Epub 2014 Oct 20. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 25329696 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abram CL, Lowell CA. The expanding role for ITAM-based signaling pathways in immune cells. Sci STKE. 2007;2007:re2. - PubMed
-
- Fathman CG, Lineberry NB. Molecular mechanisms of CD4+ T-cell anergy. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:599–609. - PubMed
-
- Hamerman JA, Lanier LL. Inhibition of immune responses by ITAM-bearing receptors. Sci STKE. 2006;2006:re1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

