MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in human cholangiocarcinoma and regulates programmed cell death 4 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3
- PMID: 19296468
- PMCID: PMC3124086
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.22838
MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in human cholangiocarcinoma and regulates programmed cell death 4 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3
Abstract
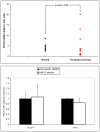
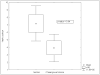
Cholangiocarcinomas (CCAs) are aggressive cancers, with high mortality and poor survival rates. Only radical surgery offers patients some hope of cure; however, most patients are not surgical candidates because of late diagnosis secondary to relatively poor accuracy of diagnostic means. MicroRNAs (miRs) are involved in every cancer examined, but they have not been evaluated in primary CCA. In this study, miR arrays were performed on five primary CCAs and five normal bile duct specimens (NBDs). Several miRs were dysregulated and miR-21 was overexpressed in CCAs. miR-21 differential expression in these 10 specimens was verified by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). To validate these findings, qRT-PCR for miR-21 was then performed on 18 additional primary CCAs and 12 normal liver specimens. MiR-21 was 95% sensitive and 100% specific in distinguishing between CCA and normal tissues, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.995. Inhibitors of miR-21 increased protein levels of programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 3 (TIMP3). Notably, messenger RNA levels of TIMP3 were significantly lower in CCAs than in normals.
Conclusions: MiR-21 is overexpressed in human CCAs. Furthermore, miR-21 may be oncogenic, at least in part, by inhibiting PDCD4 and TIMP3. Finally, these data suggest that TIMP3 is a candidate tumor suppressor gene in the biliary tree.
Figures





References
-
- de Groen PC, Gores GJ, LaRusso NF, Gunderson LL, Nagorney DM. Biliary tract cancers. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1368–78. - PubMed
-
- Shaib Y, El-Serag HB. The epidemiology of cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2004;24:115–25. - PubMed
-
- Patel T. Increasing incidence and mortality of primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in the United States. Hepatology. 2001;33:1353–7. - PubMed
-
- Farley DR, Weaver AL, Nagorney DM. “Natural history” of unresected cholangiocarcinoma: patient outcome after noncurative intervention. Mayo Clin Proc. 1995;70:425–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
