Chromosomal aberrations in UVB-induced tumors of immunosuppressed mice
- PMID: 19296524
- PMCID: PMC2739622
- DOI: 10.1002/gcc.20657
Chromosomal aberrations in UVB-induced tumors of immunosuppressed mice
Abstract
In immunocompromised individuals, such as organ transplant recipients, the risk of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) is increased 60-250 fold, and there is an increased likelihood to develop aggressive, metastatic SCC. An understanding of the genes involved in SCC tumorigenesis is critical to prevent SCC-associated morbidity and mortality. Mouse models show that different immunosuppressive drugs lead to SCCs varying in size, number, and malignant potential. In this study, we used mouse models that mimic adult transplant recipients to study the effect of immunosuppressive drugs and UV light on SCC development. UV-induced tumors from six treatment groups, control, tacrolimus (Tac), rapamycin (Rap), cyclosporin (CsA), mycophenolate mofetil (MMF), and Rap plus CsA, were evaluated by array comparative genomic hybridization. Mouse SCCs appear to show similar genomic aberrations as those reported in human SCCs and offer the ability to identify genomic changes associated with specific and combinatorial effects of drugs. Fewer aberrations were seen in tumors of mice treated with MMF or Rap. Tumors from Tac-treated animals showed the highest number of changes. Calcineurin inhibitors (Tac and CsA) did not cluster together by their genomic aberrations, indicating their contribution to UV mediated carcinogenesis may be through different pathways. The combination treatment (Rap plus CsA) did not cluster with either treatment individually, suggesting it may influence SCC tumorigenesis via a different mechanism. Future studies will identify specific genes mapping to regions of aberration that are different between treatment groups to identify target pathways that may be affected by these drugs.
Figures


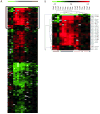
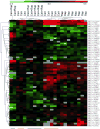
References
-
- Al-Daraji WI, Grant KR, Ryan K, Saxton A, Reynolds NJ. Localization of calcineurin/NFAT in human skin and psoriasis and inhibition of calcineurin/NFAT activation in human keratinocytes by cyclosporin A. J Invest Dermatol. 2002;118:779–788. - PubMed
-
- Ashton KJ, Weinstein SR, Maguire DJ, Griffiths LR. Chromosomal aberrations in squamous cell carcinoma and solar keratoses revealed by comparative genomic hybridization. Arch Dermatol. 2003;139:876–882. - PubMed
-
- Augustine JJ, Bodziak KA, Hricik DE. Use of sirolimus in solid organ transplantation. Drugs. 2007;67:369–391. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin CL, Melnikova VO, Ananthaswamy HN. P53 protein and pathogenesis of melanoma and nonmelanoma skin cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2008;624:265–282. - PubMed
-
- Berg D, Otley CC. Skin cancer in organ transplant recipients: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002;47:1–17. quiz 18-20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

