Vascular dysfunction in Type 2 diabetes: emerging targets for therapy
- PMID: 19296753
- PMCID: PMC2886972
- DOI: 10.1586/14779072.7.3.209
Vascular dysfunction in Type 2 diabetes: emerging targets for therapy
Abstract
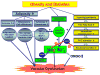
Vascular dysfunction associated with Type 2 diabetes is initially manifested in the pre-diabetic condition and continuously expressed as this complex disease progresses to include other cardiovascular complications that collectively increase patient risk to morbidity and mortality. Many factors are known to affect vascular function and this review focuses on the role of adipokines and obesity in this process. Growing evidence suggests that adipose-derived adipokines, such as cytokines, chemokines and hormones, plays a significant role in the regulation of vascular function. Inhibition of vascular reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation and lowering plasma free fatty acid level are all potential therapeutic targets for type 2 diabetes-induced vascular dysfunction. Bariatric surgery is a relatively new and more aggressive treatment for the morbidly obese patient that also results in an instant and obvious improvement of vascular function through as yet unexplained mechanisms. These therapies show great promise for the prevention and cure of diabetes-induced vascular dysfunction.
Figures
References
-
- Plutzky J, Viberti G, Haffner S. Atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance: mechanistic links and therapeutic targets. Journal of Diabetes and its Complications. 2002;16(6):401–415. - PubMed
-
- Kershaw EE, Flier JS. Adipose tissue as an endocrine organ. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89(6):2548–2556. - PubMed
-
- Mueller CF, Laude K, McNally JS, et al. Redox Mechanisms in Blood Vessels. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2005;25(2):274–278. - PubMed
-
- Kashyap SR, Belfort R, Cersosimo E, et al. Chronic low-dose lipid infusion in healthy patients induces markers of endothelial activation independent of its metabolic effects. J Cardiometab Syndr. 2008;3(3):141–146. - PubMed
-
- Gokce N, Vita JA, McDonnell M, et al. Effect of medical and surgical weight loss on endothelial vasomotor function in obese patients. The American Journal of Cardiology. 2005;95(2):266–268. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
