Molecular basis for amino acid sensing by family C G-protein-coupled receptors
- PMID: 19298394
- PMCID: PMC2697712
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2008.00078.x
Molecular basis for amino acid sensing by family C G-protein-coupled receptors
Abstract
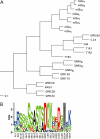
Family C of human G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) is constituted by eight metabotropic glutamate receptors, two gamma-aminobutyric acid type B (GABA(B1-2)) subunits forming the heterodimeric GABA(B) receptor, the calcium-sensing receptor, three taste1 receptors (T1R1-3), a promiscuous L-alpha;-amino acid receptor G-protein-coupled receptor family C, group 6, subtype A (GPRC6A) and seven orphan receptors. Aside from the orphan receptors, the family C GPCRs are dimeric receptors characterized by a large extracellular Venus flytrap domain which bind the endogenous agonists. Except from the GABA(B1-2) and T1R2-3 receptor, all receptors are either activated or positively modulated by amino acids. In this review, we outline mutational, biophysical and structural studies which have elucidated the interaction of the amino acids with the Venus flytrap domains, molecular mechanisms of receptor selectivity and the initial steps in receptor activation.
Figures


References
-
- Abe H, Tateyama M, Kubo Y. Functional identification of Gd3+ binding site of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1a. FEBS Lett. 2003;545:233–238. - PubMed
-
- Acher FC, Bertrand H-O. Amino acid recognition by Venus flytrap domains is encoded in an 8-residue motif. Biopolymers. 2005;80:357–366. - PubMed
-
- Bai M, Quinn S, Trivedi S, Kifor O, Pearce SHS, Pollak MR, et al. Expression and characterization of inactivating and activating mutations in the human Ca2+o-sensing receptor. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:19537–19545. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

