Vesicular transport across the fungal cell wall
- PMID: 19299133
- PMCID: PMC4282776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tim.2008.12.005
Vesicular transport across the fungal cell wall
Abstract
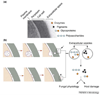
Recent findings indicate that fungi use vesicular transport to deliver substances across their cell walls. Fungal vesicles are similar to mammalian exosomes and could originate from cytoplasmic multivesicular bodies. Vesicular transport enables the export of large molecules across the cell wall, and vesicles contain lipids, proteins and polysaccharides, many of which are associated with virulence. Concentration of fungal products in vesicles could increase their efficiency in food acquisition and/or delivering potentially noxious substances to other cells, such as amoebae or phagocytes. The discovery of vesicular transport in fungi opens many new avenues for investigation in basic cell biology and pathogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- De Nobel JG, Barnett JA. Passage of molecules through yeast cell walls: a brief essay-review. Yeast. 1991;7:313–323. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson ES, Ikeda R. Effect of melanization upon porosity of the cryptococcal cell wall. Med. Mycol. 2005;43:327–333. - PubMed
-
- de Souza Pereira R, Geibel J. Direct observation of oxidative stress on the cell wall of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with atomic force microscopy. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1999;201:17–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- AI45995/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI056070/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI049371/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL059842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL059842/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI052733/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI49371/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI056070-01A2/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI52733/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI033774/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI045995/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AI033142/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

