Peripheral and visceral fat changes following a treatment switch to a non-thymidine analogue or a nucleoside-sparing regimen in HIV-infected subjects with peripheral lipoatrophy: results of ACTG A5110
- PMID: 19299471
- PMCID: PMC2721697
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkp071
Peripheral and visceral fat changes following a treatment switch to a non-thymidine analogue or a nucleoside-sparing regimen in HIV-infected subjects with peripheral lipoatrophy: results of ACTG A5110
Abstract
Background: Switching a thymidine analogue to a non-thymidine analogue or changing to a nucleoside-sparing regimen has been shown to partially reverse peripheral lipoatrophy. The current study evaluated both approaches.
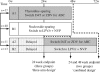
Methods: Subjects at 15 AIDS Clinical Trial Group sites receiving thymidine analogue stavudine- or zidovudine-containing regimens with plasma HIV RNA < or =500 copies/mL and lipoatrophy were prospectively randomized to: (i) switch the thymidine analogue to abacavir; (ii) discontinue all antiretrovirals and switch to lopinavir/ritonavir plus nevirapine (LPV/r+NVP); or (iii) delay switching for 24 weeks (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00028314). Single-slice computer tomography of mid-thigh and abdominal fat and metabolic and virological/immunological parameters were measured at baseline and weeks 24 and 48.
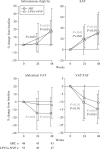
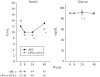
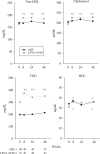
Results: Among the 101 patients enrolled, there were significant subcutaneous thigh fat and subcutaneous abdominal tissue (SAT) increases over time and decreases in visceral adipose tissue to total adipose tissue (VAT:TAT) ratios for both interventions, and a decrease in VAT for abacavir. CD4 increased in the LPV/r+NVP arm. LPV/r+NVP had a significantly shorter time to grade 3 or higher toxicity (P = 0.007), but discontinuation rates were similar. Glucose levels did not change, but insulin decreased in the LPV/r+NVP arm. Lipids tended to increase in the LPV/r+NVP arm.
Conclusions: Switching stavudine or zidovudine to a non-thymidine analogue or changing to a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-sparing regimen is associated with qualitatively similar improvements in thigh fat, SAT and VAT:TAT ratio at 48 weeks. Abacavir also resulted in VAT reductions and LPV/r+NVP resulted in CD4 count increases.
Figures

References
-
- Carr A, Samaras K, Burton S, et al. A syndrome of peripheral lipodystrophy, hyperlipidaemia and insulin resistance in patients receiving HIV protease inhibitors. AIDS. 1998;12:F51–8. - PubMed
-
- Mallon PW, Miller J, Cooper DA, et al. Prospective evaluation of the effects of antiretroviral therapy on body composition in HIV-1-infected men starting therapy. AIDS. 2003;17:971–9. - PubMed
-
- Dube MP, Parker RA, Tebas P, et al. Glucose metabolism, lipid, and body fat changes in antiretroviral-naive subjects randomized to nelfinavir or efavirenz plus dual nucleosides. AIDS. 2005;19:1807–18. - PubMed
-
- Hansen AB, Lindegaard B, Obel N, et al. Pronounced lipoatrophy in HIV-infected men receiving HAART for more than 6 years compared with the background population. HIV Med. 2006;7:38–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000096/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK059531/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027660/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI046381/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI025859/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000080/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI027665/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069513/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK049393/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK074345/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069474/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI034853/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000051/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069495/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AT003083/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI032782/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21AI063995/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI032783/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069471/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

