A multifaceted intervention to improve health worker adherence to integrated management of childhood illness guidelines in Benin
- PMID: 19299681
- PMCID: PMC2667861
- DOI: 10.2105/AJPH.2008.134411
A multifaceted intervention to improve health worker adherence to integrated management of childhood illness guidelines in Benin
Abstract
Objectives: We evaluated an intervention to support health workers after training in Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI), a strategy that can improve outcomes for children in developing countries by encouraging workers' use of evidence-based guidelines for managing the leading causes of child mortality.
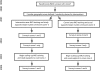
Methods: We conducted a randomized trial in Benin. We administered a survey in 1999 to assess health care quality before IMCI training. Health workers then received training plus either study supports (job aids, nonfinancial incentives, and supervision of workers and supervisors) or usual supports. Follow-up surveys conducted in 2001 to 2004 assessed recommended treatment, recommended or adequate treatment, and an index of overall guideline adherence.
Results: We analyzed 1244 consultations. Performance improved in both intervention and control groups, with no significant differences between groups. However, training proceeded slowly, and low-quality care from health workers without IMCI training diluted intervention effects. Per-protocol analyses revealed that workers with IMCI training plus study supports provided better care than did those with training plus usual supports (27.3 percentage-point difference for recommended treatment; P < .05), and both groups outperformed untrained workers.
Conclusions: IMCI training was useful but insufficient. Relatively inexpensive supports can lead to additional improvements.
Figures


References
-
- Bryce J, Boschi-Pinto C, Shibuya K, Black RE, WHO Child Health Epidemiology Reference Group. WHO estimates of the causes of death in children. Lancet 2005;365:1147–1152 - PubMed
-
- El Arifeen S, Blum LS, Hoque DME, et al. Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) in Bangladesh: early findings from a cluster-randomized study. Lancet 2004;364:1595–1602 - PubMed
-
- Armstrong Schellenberg J, Bryce J, de Savigny D, et al. The effect of Integrated Management of Childhood Illness on observed quality of care of under-fives in rural Tanzania. Health Policy Plan 2004;19:1–10 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

