Nitrated {alpha}-synuclein-induced alterations in microglial immunity are regulated by CD4+ T cell subsets
- PMID: 19299711
- PMCID: PMC2659470
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0803982
Nitrated {alpha}-synuclein-induced alterations in microglial immunity are regulated by CD4+ T cell subsets
Abstract
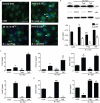
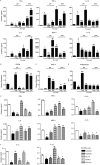
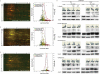
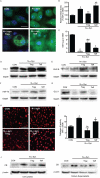
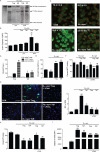
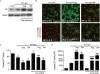
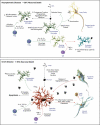
Microglial inflammatory neuroregulatory activities affect the tempo of nigrostriatal degeneration during Parkinson's disease (PD). Such activities are induced, in part, by misfolded, nitrated alpha-synuclein (N-alpha-syn) within Lewy bodies released from dying or dead dopaminergic neurons. Such pathobiological events initiate innate and adaptive immune responses affecting neurodegeneration. We posit that the neurobiological activities of activated microglia are affected by cell-protein and cell-cell contacts, in that microglial interactions with N-alpha-syn and CD4(+) T cells substantively alter the microglial proteome. This leads to alterations in cell homeostatic functions and disease. CD4(+)CD25(+) regulatory T cells suppress N-alpha-syn microglial-induced reactive oxygen species and NF-kappaB activation by modulating redox-active enzymes, cell migration, phagocytosis, and bioenergetic protein expression and cell function. In contrast, CD4(+)CD25(-) effector T cells exacerbate microglial inflammation and induce putative neurotoxic responses. These data support the importance of adaptive immunity in the regulation of Parkinson's disease-associated microglial inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proteomic studies of nitrated alpha-synuclein microglia regulation by CD4+CD25+ T cells.J Proteome Res. 2009 Jul;8(7):3497-511. doi: 10.1021/pr9001614. J Proteome Res. 2009. PMID: 19432400 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrated alpha-synuclein-activated microglial profiling for Parkinson's disease.J Neurochem. 2008 Mar;104(6):1504-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.05087.x. Epub 2007 Nov 22. J Neurochem. 2008. PMID: 18036154
-
Nitrated alpha-synuclein and microglial neuroregulatory activities.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2008 Jun;3(2):59-74. doi: 10.1007/s11481-008-9100-z. Epub 2008 Jan 17. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18202920 Free PMC article.
-
Pathological α-synuclein exacerbates the progression of Parkinson's disease through microglial activation.Toxicol Lett. 2017 Jan 4;265:30-37. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2016.11.002. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Toxicol Lett. 2017. PMID: 27865851 Review.
-
Differentiation and regulation of CD4+ T cell subsets in Parkinson's disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Aug 17;81(1):352. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05402-0. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39153043 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Altered substrate metabolism in neurodegenerative disease: new insights from metabolic imaging.J Neuroinflammation. 2021 Oct 28;18(1):248. doi: 10.1186/s12974-021-02305-w. J Neuroinflammation. 2021. PMID: 34711251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemically modified peptides based on the membrane-proximal external region of the HIV-1 envelope induce high-titer, epitope-specific nonneutralizing antibodies in rabbits.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014 Aug;21(8):1086-93. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00320-14. Epub 2014 May 28. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24872518 Free PMC article.
-
ALS patients' regulatory T lymphocytes are dysfunctional, and correlate with disease progression rate and severity.JCI Insight. 2017 Mar 9;2(5):e89530. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.89530. JCI Insight. 2017. PMID: 28289705 Free PMC article.
-
Aging and Neurodegenerative Disease: Is the Adaptive Immune System a Friend or Foe?Front Aging Neurosci. 2020 Sep 23;12:572090. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.572090. eCollection 2020. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33173502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunization Effects of a Novel α-Synuclein-Based Peptide Epitope Vaccine in Parkinson's Disease-Associated Pathology.Vaccines (Basel). 2023 Dec 5;11(12):1820. doi: 10.3390/vaccines11121820. Vaccines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38140224 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hurtig HI, Trojanowski JQ, Galvin J, Ewbank D, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Clark CM, Glosser G, Stern MB, Gollomp SM, Arnold SE. Alpha-synuclein cortical Lewy bodies correlate with dementia in Parkinson's disease. Neurology. 2000;54:1916–1921. - PubMed
-
- Giasson BI, Duda JE, Murray IV, Chen Q, Souza JM, Hurtig HI, Ischiropoulos H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM. Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective alpha-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions. Science. 2000;290:985–989. - PubMed
-
- Krishnan S, Chi EY, Wood SJ, Kendrick BS, Li C, Garzon-Rodriguez W, Wypych J, Randolph TW, Narhi LO, Biere AL, Citron M, Carpenter JF. Oxidative dimer formation is the critical rate-limiting step for Parkinson's disease alpha-synuclein fibrillogenesis. Biochemistry. 2003;42:829–837. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U54NS43011/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS043985/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01MH64570/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 5P01NS31492/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS031492/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS043011/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2R01 NS034239/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS036126/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034239/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 NS43985/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P20RR15635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P01 MH064570/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR015635/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- 2R37 NS36126/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

