Immunologic and therapeutic synergy of IL-27 and IL-2: enhancement of T cell sensitization, tumor-specific CTL reactivity and complete regression of disseminated neuroblastoma metastases in the liver and bone marrow
- PMID: 19299733
- PMCID: PMC2730673
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0800471
Immunologic and therapeutic synergy of IL-27 and IL-2: enhancement of T cell sensitization, tumor-specific CTL reactivity and complete regression of disseminated neuroblastoma metastases in the liver and bone marrow
Abstract
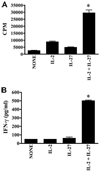
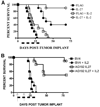
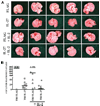
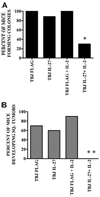
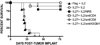
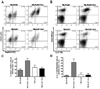
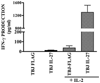
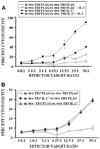
IL-27 exerts antitumor activity in murine orthotopic neuroblastoma, but only partial antitumor effect in disseminated disease. This study demonstrates that combined treatment with IL-2 and IL-27 induces potent antitumor activity in disseminated neuroblastoma metastasis. Complete durable tumor regression was achieved in 90% of mice bearing metastatic TBJ-IL-27 tumors treated with IL-2 compared with only 40% of mice bearing TBJ-IL-27 tumors alone and 0% of mice bearing TBJ-FLAG tumors with or without IL-2 treatment. Comparable antitumor effects were achieved by IL-27 protein produced upon hydrodynamic IL-27 plasmid DNA delivery when combined with IL-2. Although delivery of IL-27 alone, or in combination with IL-2, mediated pronounced regression of neuroblastoma metastases in the liver, combined delivery of IL-27 and IL-2 was far more effective than IL-27 alone against bone marrow metastases. Combined exposure to IL-27 produced by tumor and IL-2 synergistically enhances the generation of tumor-specific CTL reactivity. Potentiation of CTL reactivity by IL-27 occurs via mechanisms that appear to be engaged during both the initial sensitization and effector phase. Potent immunologic memory responses are generated in mice cured of their disseminated disease by combined delivery of IL-27 and IL-2, and depletion of CD8(+) ablates the antitumor efficacy of this combination. Moreover, IL-27 delivery can inhibit the expansion of CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory and IL-17-expressing CD4(+) cells that are otherwise observed among tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from mice treated with IL-2. These studies demonstrate that IL-27 and IL-2 synergistically induce complete tumor regression and long-term survival in mice bearing widely metastatic neuroblastoma tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Maris JM. The biologic basis for neuroblastoma heterogeneity and risk stratification. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2005;17:7–13. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein JL, Katzenstein HM, Cohn SL. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of neuroblastoma. Oncologist. 2003;8:278–292. - PubMed
-
- Redlinger RE, Jr, Mailliard RB, Lotze MT, Barksdale EM., Jr Synergistic interleukin-18 and low-dose interleukin-2 promote regression of established murine neuroblastoma in vivo. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2003;38:301–307. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu T, Berhanu A, Redlinger RE, Jr, Watkins S, Lotze MT, Barksdale EM., Jr Interleukin-12 transduced dendritic cells induce regression of established murine neuroblastoma. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2001;36:1285–1292. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

