The presence of a matrix-derived neutrophil chemoattractant in bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation
- PMID: 19299743
- PMCID: PMC4219237
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0802457
The presence of a matrix-derived neutrophil chemoattractant in bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung transplantation
Abstract
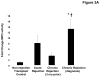
Lung transplantation is a therapeutic modality frequently used in end-stage lung disease. Unfortunately, lung transplant recipients have poor clinical outcomes, often due to the development of bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome (BOS). This process is often characterized by the pathologic findings of obliterative bronchiolitis: neutrophil influx and extracellular matrix remodeling leading to luminal obstruction and airway inflammation. The molecular mechanisms underlying BOS are poorly understood and disease-specific biomarkers are lacking. We report that in addition to increased levels of IL-8, the level of the neutrophil chemoattractant proline-glycine-proline (PGP) is elevated in BOS patient bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. The enzymes responsible for generating PGP, matrix metalloproteases 8 and -9 and prolyl endopeptidase, are also elevated in these samples. Together, IL-8 and PGP account for most of the neutrophil chemoattractant capacity seen in BOS BAL fluid. Using specific neutralizing Abs to both IL-8 and PGP, we demonstrate that PGP is a prominent neutrophil chemoattractant found in BAL fluid from individuals at the time of diagnosis of BOS. These findings highlight the influence of a matrix-derived neutrophil chemoattractant in posttransplantation BOS and provide opportunities for the development of unique diagnostics and therapeutics to potentially improve disease outcomes.
Figures


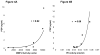
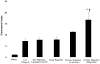
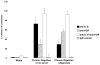

References
-
- Arcasoy SM, Kotloff RM. Lung transplantation. NEJM. 1999;340:1081–1089. - PubMed
-
- Trulock EP, Edwards LB, Taylor DO, Boucek MM, Keck BM, Hertz MI. Registry of the international society for heart and lung transplantation: Twenty-third official adult lung and heart-lung transplantation report 2006. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2006;25:880–892. - PubMed
-
- Estenne M, Maurer JR, Boehler A, Egan JJ, Frost A, Hertz MI, Mallory GB, Snell GI, Yousem S. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome 2001: An update of the diagnostic criteria. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation. 2002;21:297–310. - PubMed
-
- Estenne M, Hertz MI. Bronchiolitis obliterans after human lung transplantation. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:440–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- S10 RR019231/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- HL090999/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32A107493/PHS HHS/United States
- P30 DK074038/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL07783/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013148/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102371/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AT000477/AT/NCCIH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA13148/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL090999/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL077783/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA100949/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR050948/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

