Mimicking Ndc80 phosphorylation triggers spindle assembly checkpoint signalling
- PMID: 19300438
- PMCID: PMC2683709
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.62
Mimicking Ndc80 phosphorylation triggers spindle assembly checkpoint signalling
Abstract
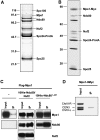
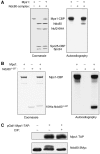
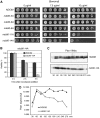
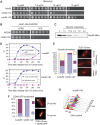
The protein kinase Mps1 is, among others, essential for the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC). We found that Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mps1 interacts physically with the N-terminal domain of Ndc80 (Ndc80(1-257)), a constituent of the Ndc80 kinetochore complex. Furthermore, Mps1 effectively phosphorylates Ndc80(1-257) in vitro and facilitates Ndc80 phosphorylation in vivo. Mutating 14 of the phosphorylation sites to alanine results in compromised checkpoint signalling upon nocodazole treatment of mutants. Mutating the identical sites to aspartate (to simulate constitutive phosphorylation) causes a metaphase arrest with wild-type-like bipolar kinetochore-microtubule attachment. This arrest is due to a constitutively active SAC and consequently the inviable aspartate mutant can be rescued by disrupting SAC signalling. Therefore, we conclude that a putative Mps1-dependent phosphorylation of Ndc80 is important for SAC activation at kinetochores.
Figures


References
-
- Ahonen LJ, Kallio MJ, Daum JR, Bolton M, Manke IA, Yaffe MB, Stukenberg PT, Gorbsky GJ (2005) Polo-like kinase 1 creates the tension-sensing 3F3/2 phosphoepitope and modulates the association of spindle-checkpoint proteins at kinetochores. Curr Biol 15: 1078–1089 - PubMed
-
- Chan GK, Liu ST, Yen TJ (2005) Kinetochore structure and function. Trends Cell Biol 15: 589–598 - PubMed
-
- Cheeseman IM, Anderson S, Jwa M, Green EM, Kang J, Yates JR III, Chan CS, Drubin DG, Barnes G (2002) Phospho-regulation of kinetochore-microtubule attachments by the Aurora kinase Ipl1p. Cell 111: 163–172 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

