A genome-wide association study in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): identification of two major susceptibility loci
- PMID: 19300482
- PMCID: PMC2650282
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000421
A genome-wide association study in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): identification of two major susceptibility loci
Abstract
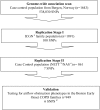
There is considerable variability in the susceptibility of smokers to develop chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). The only known genetic risk factor is severe deficiency of alpha(1)-antitrypsin, which is present in 1-2% of individuals with COPD. We conducted a genome-wide association study (GWAS) in a homogenous case-control cohort from Bergen, Norway (823 COPD cases and 810 smoking controls) and evaluated the top 100 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in the family-based International COPD Genetics Network (ICGN; 1891 Caucasian individuals from 606 pedigrees) study. The polymorphisms that showed replication were further evaluated in 389 subjects from the US National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) and 472 controls from the Normative Aging Study (NAS) and then in a fourth cohort of 949 individuals from 127 extended pedigrees from the Boston Early-Onset COPD population. Logistic regression models with adjustments of covariates were used to analyze the case-control populations. Family-based association analyses were conducted for a diagnosis of COPD and lung function in the family populations. Two SNPs at the alpha-nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (CHRNA 3/5) locus were identified in the genome-wide association study. They showed unambiguous replication in the ICGN family-based analysis and in the NETT case-control analysis with combined p-values of 1.48 x 10(-10), (rs8034191) and 5.74 x 10(-10) (rs1051730). Furthermore, these SNPs were significantly associated with lung function in both the ICGN and Boston Early-Onset COPD populations. The C allele of the rs8034191 SNP was estimated to have a population attributable risk for COPD of 12.2%. The association of hedgehog interacting protein (HHIP) locus on chromosome 4 was also consistently replicated, but did not reach genome-wide significance levels. Genome-wide significant association of the HHIP locus with lung function was identified in the Framingham Heart study (Wilk et al., companion article in this issue of PLoS Genetics; doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000429). The CHRNA 3/5 and the HHIP loci make a significant contribution to the risk of COPD. CHRNA3/5 is the same locus that has been implicated in the risk of lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Murray CJ, Lopez AD. Alternative projections of mortality and disability by cause 1990–2020: Global Burden of Disease Study. Lancet. 1997;349:1498–1504. - PubMed
-
- Cigarette smoking and health. American Thoracic Society. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1996;153:861–865. - PubMed
-
- Burrows B, Knudson RJ, Cline MG, Lebowitz MD. Quantitative relationships between cigarette smoking and ventilatory function. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1977;115:195–205. - PubMed
-
- Kauffmann F, Tager IB, Munoz A, Speizer FE, Tager IB, Munoz A, et al. Familial factors related to lung function in children aged 6–10 years. Results from the PAARC epidemiologic study. Am J Epidemiol. 1989;129:1289–1299. - PubMed
-
- Lebowitz MD, Knudson RJ, Burrows B, Knudson RJ, Burrows B, et al. Family aggregation of pulmonary function measurements. American Review of Respiratory Disease. 1984;129:8–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- N01 HR076103/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL083069/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076102/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01HL083069/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL084323/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076113/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076104/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08HL080242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076101/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076112/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076109/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076105/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076118/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- N01 HR076107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 HL080242/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076110/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL075478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076119/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076108/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076116/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076111/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01HL089856/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HR076115/HR/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084323/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- G0500306/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- N01 HR076106/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

