Studies of a ring-cleaving dioxygenase illuminate the role of cholesterol metabolism in the pathogenesis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 19300498
- PMCID: PMC2652662
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000344
Studies of a ring-cleaving dioxygenase illuminate the role of cholesterol metabolism in the pathogenesis of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
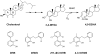
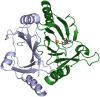
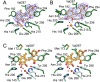
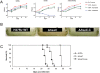
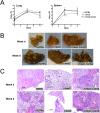
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the etiological agent of TB, possesses a cholesterol catabolic pathway implicated in pathogenesis. This pathway includes an iron-dependent extradiol dioxygenase, HsaC, that cleaves catechols. Immuno-compromised mice infected with a DeltahsaC mutant of M. tuberculosis H37Rv survived 50% longer than mice infected with the wild-type strain. In guinea pigs, the mutant disseminated more slowly to the spleen, persisted less successfully in the lung, and caused little pathology. These data establish that, while cholesterol metabolism by M. tuberculosis appears to be most important during the chronic stage of infection, it begins much earlier and may contribute to the pathogen's dissemination within the host. Purified HsaC efficiently cleaved the catecholic cholesterol metabolite, DHSA (3,4-dihydroxy-9,10-seconandrost-1,3,5(10)-triene-9,17-dione; k(cat)/K(m) = 14.4+/-0.5 microM(-1) s(-1)), and was inactivated by a halogenated substrate analogue (partition coefficient<50). Remarkably, cholesterol caused loss of viability in the DeltahsaC mutant, consistent with catechol toxicity. Structures of HsaC:DHSA binary complexes at 2.1 A revealed two catechol-binding modes: bidentate binding to the active site iron, as has been reported in similar enzymes, and, unexpectedly, monodentate binding. The position of the bicyclo-alkanone moiety of DHSA was very similar in the two binding modes, suggesting that this interaction is a determinant in the initial substrate-binding event. These data provide insights into the binding of catechols by extradiol dioxygenases and facilitate inhibitor design.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
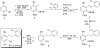
References
-
- Clark-Curtiss JE, Haydel SE. Molecular genetics of Mycobacterium tuberculosis pathogenesis. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003;57:517–549. - PubMed
-
- Wright A, Bai G, Barrera L, Boulahbal F, Martín-Casabona N, et al. Emergence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis with Extensive Resistance to Second-Line Drugs — Worldwide, 2000–2004. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2006. pp. 301–305. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

