A review of modafinil film-coated tablets for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents
- PMID: 19300563
- PMCID: PMC2654790
A review of modafinil film-coated tablets for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents
Abstract
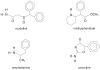
Modafinil, a wakefulness-promoting agent unrelated to classical sympathomimetic stimulants, has been studied in a total of 933 children and adolescents as a treatment for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Several studies, including three double-blind, placebo-controlled studies with intent-to-treat analyses, have demonstrated the efficacy of modafinil film-coated tablets in reducing symptoms of ADHD and associated problem behaviors in children and adolescents. Modafinil is generally well tolerated, with adverse events (such as insomnia, headache, loss of appetite, weight loss, and gastrointestinal discomfort) that are generally mild to moderate, rarely leading to medication discontinuation. To minimize treatment-emergent side effects, titration to the target dose of 355-425 mg once a day should take place over 2-3 weeks. Due to reports of skin rash (including one case of possible erythema multiforme/Stevens Johnson Syndrome during pivotal studies), additional studies have been requested to better evaluate the risks of developing severe cutaneous adverse reactions.
Keywords: adolescents; attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder; behavior; children; modafinil; treatment.
Figures







References
-
- Akaoka H, Roussel B, Lin JS, et al. Effect of modafinil and amphetamine on the ratcatecholinergic neuron activity. Neurosci Lett. 1991;123:20–2. - PubMed
-
- Arnsten AF. Stimulants:Therapeutic actions in ADHD. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006 E-pub ahead of print. - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Swanson JM, Wigal SB, et al. Efficacy and safety of modafinil film-coated tablets in children and adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder:results of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose study. Pediatrics. 2005;116:e777–84. - PubMed
-
- Biederman J, Swanson JM, Wigal SB, et al. A comparison of once-daily and divided doses of modafinil in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder:a randomized, double-blind, and placebo-controlled study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2006;67:727–35. - PubMed
-
- Brown RT, Amler RW, Freeman WS, et al. Treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder:overview of the evidence. Pediatrics. 2005;115:e749–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

