Protein components of the microRNA pathway and human diseases
- PMID: 19301657
- PMCID: PMC2903565
- DOI: 10.1007/978-1-60327-547-7_18
Protein components of the microRNA pathway and human diseases
Abstract
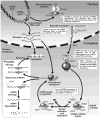
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key regulators of messenger RNA (mRNA) translation known to be involved in a wide variety of cellular processes. In fact, their individual importance is reflected in the diseases that may arise upon the loss, mutation or dysfunction of specific miRNAs. It has been appreciated only recently that diseases may also develop when the protein components of the miRNA machinery itself are affected. The core enzymes of the major protein complexes involved in miRNA biogenesis and function, such as the ribonucleases III (RNases III) Drosha and Dicer as well as Argonaute 2 (Ago2), appear to be essential. However, the accessory proteins of the miRNA pathway, such as the DiGeorge syndrome critical region gene 8 (DGCR8) protein, Exportin-5 (Exp-5), TAR RNA binding protein (TRBP) and fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP), are each related, in various ways, to specific genetic diseases.
Figures
References
-
- Miranda KC, Huynh T, Tay Y, Ang YS, Tam WL, Thomson AM, Lim B, Rigoutsos I. A pattern-based method for the identification of MicroRNA binding sites and their corresponding heteroduplexes. Cell. 2006;126:1203–1217. - PubMed
-
- Vella MC, Reinert K, Slack FJ. Architecture of a validated microRNA:target interaction. Chem Biol. 2004;11:1619–1623. - PubMed
-
- Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, Yatabe Y, Kawahara K, Sekido Y, Takahashi T. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005;65:9628–9632. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

