Common themes emerge in the transcriptional control of T helper and developmental cell fate decisions regulated by the T-box, GATA and ROR families
- PMID: 19302139
- PMCID: PMC2669811
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2008.03040.x
Common themes emerge in the transcriptional control of T helper and developmental cell fate decisions regulated by the T-box, GATA and ROR families
Abstract
Cellular differentiation requires the precise action of lineage-determining transcription factors. In the immune system, CD4(+) T helper cells differentiate into at least three distinct effector lineages, T helper type 1 (Th1), Th2 and Th17, with the fate of the cell at least in part determined by the transcription factors T-box expressed in T cells (T-bet), GATA-3 and retinoid-related orphan receptor gammat (RORgammat), respectively. Importantly, these transcription factors are members of larger families that are required for numerous developmental transitions from early embryogenesis into adulthood. Mutations in members of these transcription factor families are associated with a number of human genetic diseases due to a failure in completing lineage-specification events when the factor is dysregulated. Mechanistically, there are both common and distinct functional activities that are utilized by T-box, GATA and ROR family members to globally alter the cellular gene expression profiles at specific cell fate decision checkpoints. Therefore, understanding the molecular events that contribute to the ability of T-bet, GATA-3 and RORgammat to define T helper cell lineages can provide valuable information relevant to the establishment of other developmental systems and, conversely, information from diverse developmental systems may provide unexpected insights into the molecular mechanisms utilized in T helper cell differentiation.
Figures
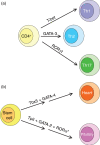
References
-
- Naiche LA, Harrelson Z, Kelly RG, Papaioannou VE. T-box genes in vertebrate development. Annu Rev Genet. 2005;17:219–39. - PubMed
-
- Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, Tadokoro CE, Lepelley A, Lafaille JJ, Cua DJ, Littman DR. The orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell. 2006;126:1121–33. - PubMed
-
- Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X, Fathman CG, Glimcher LH. A novel transcription factor, T-bet directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell. 2000;100:655–69. - PubMed
-
- Zheng W, Flavell RA. The transcription factor GATA-3 is necessary and sufficient for Th2 cytokine gene expression in CD4 T cells. Science. 1997;89:587–96. - PubMed
-
- Chang JT, Reiner SL. Specifying helper T cell fates during immunity. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2008;46:19–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

