Neuroprotective activities of activated protein C mutant with reduced anticoagulant activity
- PMID: 19302148
- PMCID: PMC2692517
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06664.x
Neuroprotective activities of activated protein C mutant with reduced anticoagulant activity
Retraction in
-
RETRACTION: Neuroprotective Activities of Activated Protein C Mutant With Reduced Anticoagulant Activity.Eur J Neurosci. 2024 Nov;60(10):6588. doi: 10.1111/ejn.16587. Epub 2024 Oct 29. Eur J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39473034 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
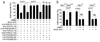
The anticoagulant activated protein C (APC) protects neurons and endothelium via protease activated receptor (PAR)1, PAR3 and endothelial protein C receptor. APC is neuroprotective in stroke models. Bleeding complications may limit the pharmacologic utility of APC. Here, we compared the 3K3A-APC mutant with 80% reduced anticoagulant activity and wild-type (wt)-APC. Murine 3K3A-APC compared with wt-APC protected mouse cortical neurons from N-methyl-D-aspartate-induced apoptosis with twofold greater efficacy and more potently reduced N-methyl-D-aspartate excitotoxic lesions in vivo. Human 3K3A-APC protected human brain endothelial cells (BECs) from oxygen/glucose deprivation with 1.7-fold greater efficacy than wt-APC. 3K3A-APC neuronal protection required PAR1 and PAR3, as shown by using PAR-specific blocking antibodies and PAR1- and PAR3-deficient cells and mice. BEC protection required endothelial protein C receptor and PAR1. In neurons and BECs, 3K3A-APC blocked caspase-9 and -3 activation and induction of p53, and decreased the Bax/Bcl-2 pro-apoptotic ratio. After distal middle cerebral artery occlusion (dMCAO) in mice, murine 3K3A-APC compared with vehicle given 4:00 h after dMCAO improved the functional outcome and reduced the infarction volume by 50% within 3 days. 3K3A-APC compared with wt-APC multi-dosing therapy at 12:00 h, 1, 3, 5 and 7 days after dMCAO significantly improved functional recovery and reduced the infarction volume by 75% and 38%, respectively, within 7 days. The wt-APC, but not 3K3A-APC, significantly increased the risk of intracerebral bleeding as indicated by a 50% increase in hemoglobin levels in the ischemic hemisphere. Thus, 3K3A-APC offers a new approach for safer and more efficacious treatments of neurodegenerative disorders and stroke with APC.
Figures



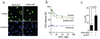



References
-
- Balcaitis S, Xie Y, Weinstein JR, Andersen H, Hanisch UK, Ransom BR, Moller T. Expression of proteinase-activated receptors in mouse microglial cells. Neuroreport. 2003;14:2373–2377. - PubMed
-
- Bernard GR, Vincent JL, Laterre PF, LaRosa SP, Dhainaut JF, Lopez-Rodriguez A, Steingrub JS, Garber GE, Helterbrand JD, Ely EW, Fisher CJ., Jr Efficacy and safety of recombinant human activated protein C for severe sepsis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001;344:699–709. - PubMed
-
- Brewer GJ, Torricelli JR, Evege EK, Price PJ. Optimized survival of hippocampal neurons in B27-supplemented Neurobasal, a new serum-free medium combination. J. Neurosci. Res. 1993;35:567–576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

