Down-regulation of cIAP2 enhances 5-FU sensitivity through the apoptotic pathway in human colon cancer cells
- PMID: 19302291
- PMCID: PMC11159709
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01112.x
Down-regulation of cIAP2 enhances 5-FU sensitivity through the apoptotic pathway in human colon cancer cells
Abstract
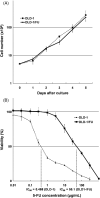
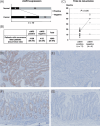
Currently 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) plays a central role in the chemotherapeutic regimens for colorectal cancers and thus it is important to understand the mechanisms that determine 5-FU sensitivity. The expression profiles of human colon cancer cell line DLD-1, its 5-FU-resistant subclone DLD-1/FU and a further 21 types of colon cancer cell lines were compared to identify the novel genes defining the sensitivity to 5-FU and to estimate which population of genes is responsible for 5-FU sensitivity. In the hierarchical clustering, DLD-1 and DLD-1/FU were most closely clustered despite over 100 times difference in their 50% inhibitory concentration of 5-FU. In DLD-1/FU, the population of genes differentially expressed compared to DLD-1 was limited to 3.3%, although it ranged from 4.8% to 24.0% in the other 21 cell lines, thus indicating that the difference of 5-FU sensitivity was defined by a limited number of genes. Next, the role of the cellular inhibitor of apoptosis 2 (cIAP2) gene, which was up-regulated in DLD-1/FU, was investigated for 5-FU resistance using RNA interference. The down-regulation of cIAP2 efficiently enhanced 5-FU sensitivity, the activation of caspase 3/7 and apoptosis under exposure to 5-FU. The immunohistochemistry of cIAP2 in cancer and corresponding normal tissues from colorectal cancer patients in stage III revealed that cIAP2 was more frequently expressed in cancer tissues than in normal tissues, and cIAP2-positive patients had a trend toward early recurrence after fluorouracil-based chemotherapy. Although the association between drug sensitivity and the IAP family in colorectal cancer has not yet been discussed, cIAP2 may therefore play an important role as a target therapy in colorectal cancer.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Overexpression of cIAP2 contributes to 5-FU resistance and a poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Br J Cancer. 2011 Oct 25;105(9):1322-30. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.387. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Br J Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21952624 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of lncRNA CCAT1 enhances 5-fluorouracil sensitivity in human colon cancer cells.BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019 Apr 23;20(1):9. doi: 10.1186/s12860-019-0188-1. BMC Mol Cell Biol. 2019. PMID: 31039730 Free PMC article.
-
Combination of the histone deacetylase inhibitor depsipeptide and 5-fluorouracil upregulates major histocompatibility complex class II and p21 genes and activates caspase-3/7 in human colon cancer HCT-116 cells.Oncol Rep. 2016 Oct;36(4):1875-85. doi: 10.3892/or.2016.5008. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Oncol Rep. 2016. PMID: 27509880 Free PMC article.
-
cIAP2 as a therapeutic target in colorectal cancer and other malignancies.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009 Nov;13(11):1333-45. doi: 10.1517/14728220903277256. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2009. PMID: 19793002 Review.
-
MicroRNA-23a antisense enhances 5-fluorouracil chemosensitivity through APAF-1/caspase-9 apoptotic pathway in colorectal cancer cells.J Cell Biochem. 2014 Apr;115(4):772-84. doi: 10.1002/jcb.24721. J Cell Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24249161
Cited by
-
The emerging role of long non-coding RNAs in the drug resistance of colorectal cancer.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018 Oct 1;11(10):4735-4743. eCollection 2018. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2018. PMID: 31949549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
5-Fluorouracil-loaded poly(ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles combined with phage E gene therapy as a new strategy against colon cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:95-107. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S26401. Epub 2012 Jan 9. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22275826 Free PMC article.
-
Folic Acid-Metabolizing Enzymes Regulate the Antitumor Effect of 5-Fluoro-2'-Deoxyuridine in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines.PLoS One. 2016 Sep 29;11(9):e0163961. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163961. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27685866 Free PMC article.
-
Global Investigations of Fusobacterium nucleatum in Human Colorectal Cancer.Front Oncol. 2019 Jul 3;9:566. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00566. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31334107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel combination treatment for colorectal cancer using Nek2 siRNA and cisplatin.Cancer Sci. 2010 May;101(5):1163-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2010.01504.x. Epub 2010 Jan 20. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 20345485 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giacchetti S, Perpoint B, Zidani R et al . Phase III multicenter randomized trial of oxaliplatin added to chronomodulated fluorouracil‐leucovorin as first‐line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 136–47. - PubMed
-
- Douillard JY, Cunningham D, Roth AD et al . Irinotecan combined with fluorouracil compared with fluorouracil alone as first‐line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: a multicentre randomised trial. Lancet 2000; 355: 1041–7. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S et al . Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan‐refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 337–45. - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W et al . Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: 2335–42. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

