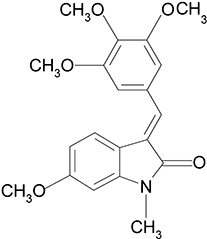
Anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting effects of C9, a new microtubule-depolymerizing agent
- PMID: 19302593
- PMCID: PMC2697741
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00112.x
Anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting effects of C9, a new microtubule-depolymerizing agent
Abstract
Background and purpose: The critical role of blood supply in the growth of solid tumours makes blood vessels an ideal target for anti-tumour drug discovery. The anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting activities of C9, a newly synthesized microtubule-depolymerizing agent, were investigated with several in vitro and in vivo models. Possible mechanisms involved in its activity were also assessed.
Experimental approach: Microtubule-depolymerizing actions were assessed by surface plasmon resonance binding, competitive inhibition and cytoskeleton immunofluorescence. Anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting activities were tested on proliferation, migration, tube formation with human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and in rat aortic ring, chick chorioallantoic membrane and Matrigel plug assays. Western blots and Rho activation assays were employed to examine the role of Raf-MEK-ERK (mitogen-activated ERK kinase, extracellular signal-regulated kinase) and Rho/Rho kinase signalling.
Key results: C9 inhibited proliferation, migration and tube formation of endothelial cells and inhibited angiogenesis in aortic ring and chick chorioallantoic membrane assays. C9 induced disassembly of microtubules in endothelial cells and down-regulated Raf-MEK-ERK signalling activated by pro-angiogenic factors. In addition, C9 disrupted capillary-like networks and newly formed vessels in vitro and rapidly decreased perfusion of neovasculature in vivo. Endothelial cell contraction and membrane blebbing induced by C9 in neovasculature was dependent on the Rho/Rho kinase pathway.
Conclusions and implications: Anti-angiogenic and vascular disruption by C9 was associated with changes in morphology and function of endothelial cells, involving the Raf-MEK-ERK and Rho/Rho kinase signalling pathways. These findings strongly suggest that C9 is a new microtubule-binding agent that could effectively target tumour vasculature.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deoxypodophyllotoxin exerts both anti-angiogenic and vascular disrupting effects.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013 Aug;45(8):1710-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.04.030. Epub 2013 May 20. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013. PMID: 23702033
-
Vascular disrupting activity of combretastatin analogues.Vascul Pharmacol. 2016 Aug;83:78-89. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2016.05.006. Epub 2016 May 25. Vascul Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27235861
-
Formononetin, a novel FGFR2 inhibitor, potently inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in preclinical models.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 29;6(42):44563-78. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6310. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26575424 Free PMC article.
-
Antivascular actions of microtubule-binding drugs.Clin Cancer Res. 2009 Apr 15;15(8):2594-601. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2710. Epub 2009 Apr 7. Clin Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19351751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen sulphide and angiogenesis: mechanisms and applications.Br J Pharmacol. 2011 Oct;164(3):853-65. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.01191.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21198548 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Newly discovered angiogenesis inhibitors and their mechanisms of action.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012 Sep;33(9):1103-11. doi: 10.1038/aps.2012.97. Epub 2012 Aug 27. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012. PMID: 22922347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Curcumin induces DNA damage and caffeine-insensitive cell cycle arrest in colorectal carcinoma HCT116 cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2011 Aug;354(1-2):247-52. doi: 10.1007/s11010-011-0824-3. Epub 2011 Apr 28. Mol Cell Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21526346
-
Engineering approaches for investigating tumor angiogenesis: exploiting the role of the extracellular matrix.Cancer Res. 2012 Dec 1;72(23):6089-96. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2773. Epub 2012 Nov 19. Cancer Res. 2012. PMID: 23172313 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PGE2 promotes angiogenesis through EP4 and PKA Cγ pathway.Blood. 2011 Nov 10;118(19):5355-64. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-04-350587. Epub 2011 Sep 16. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21926356 Free PMC article.
-
Utilisation of Chick Embryo Chorioallantoic Membrane as a Model Platform for Imaging-Navigated Biomedical Research.Cells. 2021 Feb 22;10(2):463. doi: 10.3390/cells10020463. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33671534 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alley MC, Scudiero DA, Monks A, Hursey ML, Czerwinski MJ, Fine DL, et al. Feasibility of drug screening with panels of human tumor cell lines using a microculture tetrazolium assay. Cancer Res. 1988;48:589–601. - PubMed
-
- Ashton AW, Yokota R, John G, Zhao S, Suadicani SO, Spray DC, et al. Inhibition of endothelial cell migration, intercellular communication, and vascular tube formation by thromboxane A(2) J Biol Chem. 1999;274:35562–35570. - PubMed
-
- Belleri M, Ribatti D, Nicoli S, Cotelli F, Forti L, Vannini V, et al. Antiangiogenic and vascular-targeting activity of the microtubule-destabilizing trans-resveratrol derivative 3,5,4′-trimethoxystilbene. Mol Pharmacol. 2005;67:1451–1459. - PubMed
-
- Bergers G, Javaherian K, Lo KM, Folkman J, Hanahan D. Effects of angiogenesis inhibitors on multistage carcinogenesis in mice. Science. 1999;284:808–812. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

