Enlarged extracellular space of aquaporin-4-deficient mice does not enhance diffusion of Alexa Fluor 488 or dextran polymers
- PMID: 19303428
- PMCID: PMC2853363
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.03.017
Enlarged extracellular space of aquaporin-4-deficient mice does not enhance diffusion of Alexa Fluor 488 or dextran polymers
Abstract
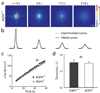
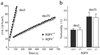
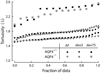
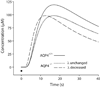
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) water channels expressed on glia have been implicated in maintaining the volume of extracellular space (ECS). A previous diffusion study employing small cation tetramethylammonium and a real-time iontophoretic (RTI) method demonstrated an increase of about 25% in the ECS volume fraction (alpha) in the neocortex of AQP4(-/-) mice compared to AQP4(+/+) mice but no change in the hindrance imposed to diffusing molecules (tortuosity lambda). In contrast, other diffusion studies employing large molecules (dextran polymers) and a fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) method measured a decrease of about 10%-20% in lambda in the neocortex of AQP4(-/-) mice. These conflicting findings on lambda would imply that large molecules diffuse more readily in the enlarged ECS of AQP4(-/-) mice than in wild type but small molecules do not. To test this hypothesis, we used integrative optical imaging (IOI) to measure tortuosity with a small Alexa Fluor 488 (molecular weight [MW] 547, lambda(AF)) and two large dextran polymers (MW 3000, lambda(dex3) and MW 75,000, lambda(dex75)) in the in vitro neocortex of AQP4(+/+) and AQP4(-/-) mice. We found that lambda(AF)=1.59, lambda(dex3)=1.76 and lambda(dex75)=2.30 obtained in AQP4(-/-) mice were not significantly different from lambda(AF)=1.61, lambda(dex3)=1.76, and lambda(dex75)=2.33 in AQP4(+/+) mice. These IOI results demonstrate that lambda measured with small and large molecules each remain unchanged in the enlarged ECS of AQP4(-/-) mice compared to values in AQP4(+/+) mice. Further analysis suggests that the FRAP method yields diffusion parameters not directly comparable with those obtained by IOI or RTI methods. Our findings have implications for the role of glial AQP4 in maintaining the ECS structure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aquaporin-4-deficient mice have increased extracellular space without tortuosity change.J Neurosci. 2008 May 21;28(21):5460-4. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0257-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18495879 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion of flexible random-coil dextran polymers measured in anisotropic brain extracellular space by integrative optical imaging.Biophys J. 2008 Aug;95(3):1382-92. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.124743. Epub 2008 May 2. Biophys J. 2008. PMID: 18456831 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular diffusion is fast and isotropic in the stratum radiatum of hippocampal CA1 region in rat brain slices.Hippocampus. 2005;15(4):441-50. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20068. Hippocampus. 2005. PMID: 15719413
-
Diffusion of molecules in brain extracellular space: theory and experiment.Prog Brain Res. 2000;125:129-54. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(00)25007-3. Prog Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11098654 Review.
-
Diffusion in brain extracellular space.Physiol Rev. 2008 Oct;88(4):1277-340. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00027.2007. Physiol Rev. 2008. PMID: 18923183 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrity of White Matter is Compromised in Mice with Hyaluronan Deficiency.Neurochem Res. 2020 Jan;45(1):53-67. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02819-z. Epub 2019 Jun 7. Neurochem Res. 2020. PMID: 31175541 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of alpha-syntrophin deletion on the changes in tissue structure and extracellular diffusion associated with cell swelling under physiological and pathological conditions.PLoS One. 2013 Jul 5;8(7):e68044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068044. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23861848 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Extracellular Space: The Final Frontier of Neuroscience.Biophys J. 2017 Nov 21;113(10):2133-2142. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2017.06.052. Epub 2017 Jul 26. Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 28755756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gliotoxin-induced swelling of astrocytes hinders diffusion in brain extracellular space via formation of dead-space microdomains.Glia. 2014 Jul;62(7):1053-65. doi: 10.1002/glia.22661. Epub 2014 Mar 31. Glia. 2014. PMID: 24687699 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time Iontophoresis with Tetramethylammonium to Quantify Volume Fraction and Tortuosity of Brain Extracellular Space.J Vis Exp. 2017 Jul 24;(125):55755. doi: 10.3791/55755. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28784968 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M, Ottersen OP. The molecular basis of water transport in the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:991–1001. - PubMed
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M, Otsuka T, Hurn PD, Traystman RJ, Haug FM, Froehner SC, Adams ME, Neely JD, Agre P, Ottersen OP, Bhardwaj A. An alpha-syntrophin-dependent pool of AQP4 in astroglial end-feet confers bidirectional water flow between blood and brain. Proc. Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:2106–2111. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M, Xue R, Haug FM, Neely JD, Bhardwaj A, Agre P, Adams ME, Froehner SC, Mori S, Ottersen OP. Alpha syntrophin deletion removes the perivascular but not the endothelial pool of aqaporin-4 at the blood-brain barrier and delays the development of brain edema in an experimental model of acute hyponatremia. FASEB J. 2004a;18:542–544. - PubMed
-
- Amiry-Moghaddam M, Frydenlung DS, Ottersen OP. Anchoring of aquaporin-4 in brain: molecular mechanism and implications for the physiology and pathophysiology of water transport. Neuroscience. 2004b;129:999–1010. - PubMed
-
- Anděrová M, Kubinová S, Mazel T, Chvátal A, Eliasson C, Pěkný M, Syková E. Effect of elevated K+, hypotonic stress, and cortical spreading depression on astrocyte swelling in GFAP-deficient mice. Glia. 2001;35:189–203. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

