Substituted imidazopyridines as potent inhibitors of HCV replication
- PMID: 19303654
- PMCID: PMC7114863
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2008.12.028
Substituted imidazopyridines as potent inhibitors of HCV replication
Abstract
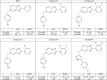
Background/aims: Following lead optimization, a set of substituted imidazopyridines was identified as potent and selective inhibitors of in vitro HCV replication. The particular characteristics of one of the most potent compounds in this series (5-[[3-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-isoxazolyl]methyl]-2-(2,3-difluorophenyl)-5H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridine or GS-327073), were studied.
Methods: Antiviral activity of GS-327073 was evaluated in HCV subgenomic replicons (genotypes 1b, 1a and 2a), in the JFH1 (genotype 2a) infectious system and against replicons resistant to various selective HCV inhibitors. Combination studies of GS-327073 with other selective HCV inhibitors were performed.
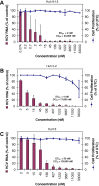
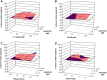
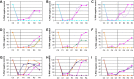
Results: Fifty percent effective concentrations for inhibition of HCV subgenomic 1b replicon replication ranged between 2 and 50 nM and were 100-fold higher for HCV genotype 2a virus. The 50% cytostatic concentrations were > or = 17 microM, thus resulting in selectivity indices of > or = 340. GS-327073 retained wild-type activity against HCV replicons that were resistant to either HCV protease inhibitors or several polymerase inhibitors. GS-327073, when combined with either interferon alpha, ribavirin, a nucleoside polymerase or a protease inhibitor resulted in overall additive antiviral activity. Combinations containing GS-327073 proved highly effective in clearing hepatoma cells from HCV.
Conclusions: GS-327073 is a potent in vitro inhibitor of HCV replication either alone or in combination with other selective HCV inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Discovery and characterization of substituted diphenyl heterocyclic compounds as potent and selective inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Apr;52(4):1419-29. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00525-07. Epub 2008 Jan 28. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008. PMID: 18227176 Free PMC article.
-
HCV NS5A replication complex inhibitors. Part 4. Optimization for genotype 1a replicon inhibitory activity.J Med Chem. 2014 Mar 13;57(5):1976-94. doi: 10.1021/jm301796k. Epub 2013 Apr 10. J Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 23573957
-
The non-immunosuppressive cyclosporin DEBIO-025 is a potent inhibitor of hepatitis C virus replication in vitro.Hepatology. 2006 Apr;43(4):761-70. doi: 10.1002/hep.21102. Hepatology. 2006. PMID: 16557546
-
Impact of ribavirin on HCV replicon RNA decline during treatment with interferon-α and the protease inhibitors boceprevir or telaprevir.Antivir Ther. 2011;16(5):695-704. doi: 10.3851/IMP1821. Antivir Ther. 2011. PMID: 21817191
-
Selective inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication.Antiviral Res. 2006 Sep;71(2-3):363-71. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2006.06.006. Epub 2006 Jun 23. Antiviral Res. 2006. PMID: 16843538 Review.
Cited by
-
Antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus: beyond the standard of care.Viruses. 2010 Apr;2(4):826-866. doi: 10.3390/v2040826. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Viruses. 2010. PMID: 21994657 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and functionality in flavivirus NS-proteins: perspectives for drug design.Antiviral Res. 2010 Aug;87(2):125-48. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2009.11.009. Epub 2009 Nov 27. Antiviral Res. 2010. PMID: 19945487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral drugs against hepatitis C virus.Genet Vaccines Ther. 2011 Jun 23;9:11. doi: 10.1186/1479-0556-9-11. Genet Vaccines Ther. 2011. PMID: 21699699 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of hepatitis C virus replication by semi-synthetic derivatives of glycopeptide antibiotics.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011 Jun;66(6):1287-94. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr104. Epub 2011 Mar 24. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011. PMID: 21436155 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in the discovery of potent RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (RdRp) inhibitors targeting viruses.RSC Med Chem. 2020 Dec 23;12(3):306-320. doi: 10.1039/d0md00318b. eCollection 2021 Mar 1. RSC Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 34046618 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Craxi A., Laffi G., Zignego A.L. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection: a systemic disease. Mol Aspects Med. 2007;29:85–95. - PubMed
-
- Fried M.W., Shiffman M.L., Reddy K.R., Smith C., Marinos C., Goncales L. Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:975–982. - PubMed
-
- Manns M.P., McHutchison J.G., Gordon S.C., Rustgi V.K., Shiffman M., Reindollar R. Peginterferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin compared with interferon alfa-2b plus ribavirin for initial treatment of chronic hepatitis C: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2001;358:958–965. - PubMed
-
- Firpi R.J., Nelson D.R. Current and future hepatitis C therapies. Arch Med Res. 2007;38:678–690. - PubMed
-
- Hayashi N., Takehara T. Antiviral therapy for chronic hepatitis C: past, present, and future. J Gastroenterol. 2006;41:17–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

