Composite S-layer lipid structures
- PMID: 19303933
- PMCID: PMC2886963
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jsb.2009.03.004
Composite S-layer lipid structures
Abstract
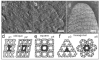
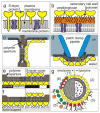
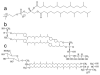
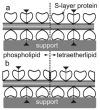
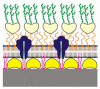
Designing and utilization of biomimetic membrane systems generated by bottom-up processes is a rapidly growing scientific and engineering field. Elucidation of the supramolecular construction principle of archaeal cell envelopes composed of S-layer stabilized lipid membranes led to new strategies for generating highly stable functional lipid membranes at meso- and macroscopic scale. In this review, we provide a state of the art survey how S-layer proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides may be used as basic building blocks for the assembly of S-layer supported lipid membranes. These biomimetic membrane systems are distinguished by a nanopatterned fluidity, enhanced stability and longevity and thus, provide a dedicated reconstitution matrix for membrane-active peptides and transmembrane proteins. Exciting areas for application of composite S-layer membrane systems concern sensor systems involving specific membrane functions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biomimetic interfaces based on S-layer proteins, lipid membranes and functional biomolecules.J R Soc Interface. 2014 May 8;11(96):20140232. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2014.0232. Print 2014 Jul 6. J R Soc Interface. 2014. PMID: 24812051 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S-layer proteins as supporting scaffoldings for functional lipid membranes.IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2004 Mar;3(1):16-21. doi: 10.1109/tnb.2004.824267. IEEE Trans Nanobioscience. 2004. PMID: 15382638 Review.
-
S-layer stabilized lipid membranes (Review).Biointerphases. 2008 Jun;3(2):FA3. doi: 10.1116/1.2889067. Biointerphases. 2008. PMID: 20408666 Free PMC article.
-
S-layers as a tool kit for nanobiotechnological applications.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007 Feb;267(2):131-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2006.00573.x. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007. PMID: 17328112 Review.
-
Nanotechnology with S-layer Proteins.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2073:195-218. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9869-2_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31612444
Cited by
-
Lactobacillus surface layer proteins: structure, function and applications.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Jun;97(12):5225-43. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-4962-2. Epub 2013 May 16. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23677442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S-layers: principles and applications.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2014 Sep;38(5):823-64. doi: 10.1111/1574-6976.12063. Epub 2014 Feb 24. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2014. PMID: 24483139 Free PMC article.
-
S-layer fusion proteins--construction principles and applications.Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011 Dec;22(6):824-31. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2011.05.510. Epub 2011 Jun 21. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21696943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of self-assembly of S-layer protein slp-B53 from Lysinibacillus sphaericus.Eur Biophys J. 2017 Jan;46(1):77-89. doi: 10.1007/s00249-016-1139-9. Epub 2016 Jun 6. Eur Biophys J. 2017. PMID: 27270294
-
Formation and characteristics of mixed lipid/polymer membranes on a crystalline surface-layer protein lattice.Biointerphases. 2020 Jan 16;15(1):011002. doi: 10.1116/1.5132390. Biointerphases. 2020. PMID: 31948239 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anrather D, Smetazko M, Saba M, Alguel Y, Schalkhammer T. Supported membrane nanodevices. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2004;4:1–22. - PubMed
-
- Arora A, Tamm LK. Biophysical approaches to membrane protein structure determinations. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2001;11:540–547. - PubMed
-
- Åvall-Jääskeläinen S, Palva A. Lactobacillus surface layers and their applications. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005;29:511–529. - PubMed
-
- Bakowsky U, Rothe U, Antonopoulos E, Martini T, Henkel L, Freisleben HJ. Monomolecular organization of the main tetraether lipid from Thermoplasma acidophilum at the water–air interface. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2000;105:31–42. - PubMed
-
- Baumeister W, Lembcke G, Dürr R, Phipps B. Electron crystallography of bacterial surface proteins. In: Freyer JR, Dorset DL, editors. Electron Crystallography of Organic Molecules. Kluwer Academic Publishers; Dortrecht: 1990. pp. 283–296.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

