Neck and face surface electromyography for prosthetic voice control after total laryngectomy
- PMID: 19304494
- PMCID: PMC3392649
- DOI: 10.1109/TNSRE.2009.2017805
Neck and face surface electromyography for prosthetic voice control after total laryngectomy
Abstract
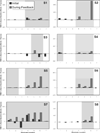
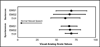
The electrolarynx (EL) is a common rehabilitative speech aid for individuals who have undergone total laryngectomy, but they typically lack pitch control and require the exclusive use of one hand. The viability of using neck and face surface electromyography (sEMG) to control the onset, offset, and pitch of an EMG-controlled EL (EMG-EL) was studied. Eight individuals who had undergone total laryngectomy produced serial and running speech using a typical handheld EL and the EMG-EL while attending to real-time visual sEMG biofeedback. Running speech tokens produced with the EMG-EL were examined for naturalness by 10 listeners relative to those produced with a typical EL using a visual analog scale. Serial speech performance was assessed as the percentage of words that were fully voiced and pauses that were successfully produced. Results of the visual analog scale assessment indicated that individuals were able to use the EMG-EL without training to produce running speech perceived as natural as that produced with a typical handheld EL. All participants were able to produce running and serial speech with the EMG-EL controlled by sEMG from multiple recording locations, with the superior ventral neck or submental surface locations providing at least one of the two best control locations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Electromyographic control of a hands-free electrolarynx using neck strap muscles.J Commun Disord. 2009 May-Jun;42(3):211-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jcomdis.2008.12.002. Epub 2009 Jan 19. J Commun Disord. 2009. PMID: 19233382 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a wireless electromyographically controlled electrolarynx voice prosthesis.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011;2011:5352-5. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2011.6091324. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2011. PMID: 22255547 Free PMC article.
-
Design and implementation of a hands-free electrolarynx device controlled by neck strap muscle electromyographic activity.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2004 Feb;51(2):325-32. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2003.820373. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2004. PMID: 14765705 Clinical Trial.
-
Electrolarynx in voice rehabilitation.Auris Nasus Larynx. 2007 Sep;34(3):327-32. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2006.11.010. Epub 2007 Jan 18. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2007. PMID: 17239553 Review.
-
Voice rehabilitation after laryngectomy.Mo Med. 1995 Mar;92(3):145-7. Mo Med. 1995. PMID: 7731448 Review.
Cited by
-
Alternative communication systems for people with severe motor disabilities: a survey.Biomed Eng Online. 2011 Apr 20;10:31. doi: 10.1186/1475-925X-10-31. Biomed Eng Online. 2011. PMID: 21507236 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent trends and challenges of surface electromyography in prosthetic applications.Biomed Eng Lett. 2023 Apr 22;13(3):353-373. doi: 10.1007/s13534-023-00281-z. eCollection 2023 Aug. Biomed Eng Lett. 2023. PMID: 37519867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vowel generation for children with cerebral palsy using myocontrol of a speech synthesizer.Front Hum Neurosci. 2015 Jan 22;8:1077. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2014.01077. eCollection 2014. Front Hum Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25657622 Free PMC article.
-
Electrically compensated, tattoo-like electrodes for epidermal electrophysiology at scale.Sci Adv. 2020 Oct 23;6(43):eabd0996. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abd0996. Print 2020 Oct. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 33097545 Free PMC article.
-
Improving Perceptual Speech Ratings: The Effects of Auditory Training on Judgments of Dysarthric Speech.J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2023 Nov 9;66(11):4236-4258. doi: 10.1044/2023_JSLHR-23-00322. Epub 2023 Sep 29. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 2023. PMID: 37774738 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2008. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2008.
-
- Gates GA, Ryan W, Cooper JC, Jr, Lawlis GF, Cantu E, Hayashi T, Lauder E, Welch RW, Hearne E. Current status of laryngectomee rehabilitation: I. Results of therapy. Am J Otolaryngol. 1982;vol. 3:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Mendenhall WM, Morris CG, Stringer SP, Amdur RJ, Hinerman RW, Villaret DB, Robbins KT. Voice rehabilitation after total laryngectomy and postoperative radiation therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2002;vol. 20:2500–2505. - PubMed
-
- Gress C, Singer M. Tracheoesophageal Voice Restoration. In: Doyle P, Keith RL, editors. Contemporary Consideration in the Treatment and Rehabilitation of Head and Neck Cancer: Voice, Speech, and Swallowing. Austin: Pro-Ed; 2005. pp. 431–452.
-
- Pou AM. Tracheoesophageal voice restoration with total laryngectomy. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2004;vol. 37:531–545. - PubMed

