Agreement between spectral-domain and time-domain OCT for measuring RNFL thickness
- PMID: 19304586
- PMCID: PMC3465953
- DOI: 10.1136/bjo.2008.150698
Agreement between spectral-domain and time-domain OCT for measuring RNFL thickness
Abstract
Background/aims: To evaluate spectral-domain (SD) optical coherence tomography (OCT) reproducibility and assess the agreement between SD-OCT and Time-Domain (TD) OCT retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL) measurements.
Methods: Three Cirrus-SD-OCT scans and one Stratus-TD-OCT scan were obtained from Diagnostic Innovations in Glaucoma Study (DIGS) healthy participants and glaucoma patients on the same day. Repeatability was evaluated using Sw (within-subject standard deviation), CV (coefficient of variation) and ICC (intraclass correlation coefficient). Agreement was assessed using correlation and Bland-Altman plots.
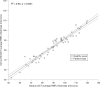
Results: 16 healthy participants (32 eyes) and 39 patients (78 eyes) were included. SD-OCT reproducibility was excellent in both groups. The CV and ICC for Average RNFL thickness were 1.5% and 0.96, respectively, in healthy eyes and 1.6% and 0.98, respectively, in patient eyes. Correlations between RNFL parameters were strong, particularly for average RNFL thickness (R(2) = 0.92 in patient eyes). Bland-Altman plots showed good agreement between instruments, with better agreement for average RNFL thickness than for sectoral RNFL parameters (for example, at 90 microm average RNFL thickness, 95% limits of agreement were -13.1 to 0.9 for healthy eyes and -16.2 to -0.3 microm for patient eyes).
Conclusions: SD-OCT measurements were highly repeatable in healthy and patient eyes. Although the agreement between instruments was good, TD-OCT provided thicker RNFL measurements than SD-OCT. Measurements with these instruments should not be considered interchangeable.
Figures


References
-
- van Velthoven ME, Faber DJ, Verbraak FD, et al. Recent developments in optical coherence tomography for imaging the retina. Progr Retin Eye Res. 2007;26:57–77. - PubMed
-
- Chen TC, Cense B, Pierce MC, et al. Spectral domain optical coherence tomography: ultra-high speed, ultra-high resolution ophthalmic imaging. Arch Ophthalmol. 2005;123:1715–20. - PubMed
-
- Wojtkowski M, Leitgeb R, Kowalczyk A, et al. In vivo human retinal imaging by Fourier domain optical coherence tomography. J Biom Opt. 2002;7:457–63. - PubMed
-
- Nassif N, Cense B, Hyle Park B, et al. In vivo human retinal imaging by ultrahigh-speed spectral domain optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett. 2004;29:480–2. - PubMed
-
- de Boer JF, Cense B, Hyle Park B, et al. Improved signal-to-noise ratio in spectral-domain compared with time-domain optical coherence tomography. Opt Lett. 2003;28:2067–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
