Characterization of a novel thermostable carboxylesterase from Geobacillus kaustophilus HTA426 shows the existence of a new carboxylesterase family
- PMID: 19304850
- PMCID: PMC2681792
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01060-08
Characterization of a novel thermostable carboxylesterase from Geobacillus kaustophilus HTA426 shows the existence of a new carboxylesterase family
Abstract
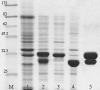
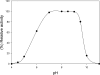
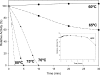
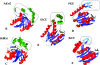
The gene GK3045 (741 bp) from Geobacillus kaustophilus HTA426 was cloned, sequenced, and overexpressed into Escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3). The deduced protein was a 30-kDa monomeric esterase with high homology to carboxylesterases from Geobacillus thermoleovorans NY (99% identity) and Geobacillus stearothermophilus (97% identity). This protein suffered a proteolytic cut in E. coli, and the problem was overcome by introducing a mutation in the gene (K212R) without affecting the activity. The resulting Est30 showed remarkable thermostability at 65 degrees C, above the optimum growth temperature of G. kaustophilus HTA426. The optimum pH of the enzyme was 8.0. In addition, the purified enzyme exhibited stability against denaturing agents, like organic solvents, detergents, and urea. The protein catalyzed the hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl esters of different acyl chain lengths, confirming the esterase activity. The sequence analysis showed that the protein contains a catalytic triad formed by Ser93, Asp192, and His222, and the Ser of the active site is located in the conserved motif Gly91-X-Ser93-X-Gly95 included in most esterases and lipases. However, this carboxylesterase showed no more than 17% sequence identity with the closest members in the eight families of microbial carboxylesterases. The three-dimensional structure was modeled by sequence alignment and compared with others carboxylesterases. The topological differences suggested the classification of this enzyme and other Geobacillus-related carboxylesterases in a new alpha/beta hydrolase family different from IV and VI.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Functional expression of a novel methanol-stable esterase from Geobacillus subterraneus DSM13552 for biocatalytic synthesis of cinnamyl acetate in a solvent-free system.BMC Biotechnol. 2020 Jun 29;20(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12896-020-00622-1. BMC Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32600313 Free PMC article.
-
A novel thermostable carboxylesterase from Geobacillus thermodenitrificans: evidence for a new carboxylesterase family.J Biochem. 2010 Sep;148(3):299-308. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvq064. Epub 2010 Jun 29. J Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20587647
-
Molecular cloning and characterization of a new and highly thermostable esterase from Geobacillus sp. JM6.J Basic Microbiol. 2015 Oct;55(10):1219-31. doi: 10.1002/jobm.201500081. Epub 2015 Jul 15. J Basic Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 26175347
-
Recent advances of structure, function, and engineering of carboxylesterases for the pharmaceutical industry: A minireview.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;307(Pt 3):142206. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.142206. Epub 2025 Mar 17. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40107535 Review.
-
Carboxylic ester hydrolases: Classification and database derived from their primary, secondary, and tertiary structures.Protein Sci. 2016 Nov;25(11):1942-1953. doi: 10.1002/pro.3016. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Protein Sci. 2016. PMID: 27530203 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
First functional and mutational analysis of group 3 N-acetylneuraminate lyases from Lactobacillus antri and Lactobacillus sakei 23K.PLoS One. 2014 May 9;9(5):e96976. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096976. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24817128 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular characterization of a novel N-acetylneuraminate lyase from Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011 Apr;77(7):2471-8. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02927-10. Epub 2011 Feb 11. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21317263 Free PMC article.
-
IcmF is a fusion between the radical B12 enzyme isobutyryl-CoA mutase and its G-protein chaperone.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 1;285(1):655-66. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.062182. Epub 2009 Oct 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19864421 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a novel lipolytic fusion biocatalyst GDEst-lip for industrial application.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Jun;44(6):799-815. doi: 10.1007/s10295-017-1905-4. Epub 2017 Jan 19. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28105534
-
Metagenomic mining for thermostable esterolytic enzymes uncovers a new family of bacterial esterases.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 19;6:38886. doi: 10.1038/srep38886. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27991516 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold, K., L. Bordoli, J. Kopp, and T. Schwede. 2006. The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22195-201. - PubMed
-
- Bornemann, S., J. M. Cassells, J. S. Dordick, and A. J. Hacking. 1992. The use of enzymes to regioselectivity deacylate sucrose esters. Biocatalysis 71-12.
-
- Bornscheuer, U. T. 2002. Microbial carboxyl esterases: classification, properties and application in biocatalysis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2673-81. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

