An orthologue of Bacteroides fragilis NanH is the principal sialidase in Tannerella forsythia
- PMID: 19304852
- PMCID: PMC2681896
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01618-08
An orthologue of Bacteroides fragilis NanH is the principal sialidase in Tannerella forsythia
Abstract
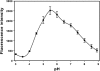
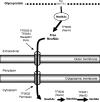
Sialidase activity is a putative virulence factor of the anaerobic periodontal pathogen Tannerella forsythia, but it is uncertain which genes encode this activity. Characterization of a putative sialidase, SiaHI, by others, indicated that this protein alone may not be responsible for all of the sialidase activity. We describe a second sialidase in T. forsythia (TF0035), an orthologue of Bacteroides fragilis NanH, and its expression in Escherichia coli. Sialidase activity of the expressed NanH was confirmed by using 2'-(4-methylumbelliferyl)-alpha-D-N-acetylneuraminic acid as a substrate. Biochemical characterization of the recombinant T. forsythia NanH indicated that it was active over a broad pH range, with optimum activity at pH 5.5. This enzyme has high affinity for 2'-(4-methylumbelliferyl)-alpha-D-N-acetylneuraminic acid (K(m) of 32.9 +/- 10.3 microM) and rapidly releases 4-methylumbelliferone (V(max) of 170.8 +/- 11.8 nmol of 4-methylumbelliferone min(-1) mg of protein(-1)). E. coli lysates containing recombinant T. forsythia NanH cleave sialic acid from a range of substrates, with a preference for alpha2-3 glycosidic linkages. The genes adjacent to nanH encode proteins apparently involved in the metabolism of sialic acid, indicating that the NanH sialidase is likely to be involved in nutrient acquisition.
Figures
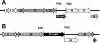

Similar articles
-
Evidence for a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) of Tannerella forsythia NanH sialidase, key to interactions at the host-pathogen interface.Biochem J. 2018 Mar 26;475(6):1159-1176. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20170592. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 29483296
-
Characterization of a recombinant Bacteroides fragilis sialidase expressed in Escherichia coli.Anaerobe. 2018 Apr;50:69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Anaerobe. 2018. PMID: 29432848
-
Characterization of a sialate-O-acetylesterase (NanS) from the oral pathogen Tannerella forsythia that enhances sialic acid release by NanH, its cognate sialidase.Biochem J. 2015 Dec 1;472(2):157-67. doi: 10.1042/BJ20150388. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Biochem J. 2015. PMID: 26378150
-
Sialic acid, periodontal pathogens and Tannerella forsythia: stick around and enjoy the feast!Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012 Feb;27(1):11-22. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1014.2011.00630.x. Epub 2011 Nov 12. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22230462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virulence mechanisms of Tannerella forsythia.Periodontol 2000. 2010 Oct;54(1):106-16. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0757.2009.00332.x. Periodontol 2000. 2010. PMID: 20712636 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
The Roles of Periodontal Bacteria in Atherosclerosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 16;24(16):12861. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612861. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37629042 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and characterization of NanH2 and NanH3, enzymes responsible for sialidase activity in the vaginal bacterium Gardnerella vaginalis.J Biol Chem. 2019 Apr 5;294(14):5230-5245. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006221. Epub 2019 Feb 5. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30723162 Free PMC article.
-
Sialidases From Clostridium perfringens and Their Inhibitors.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Jan 10;9:462. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00462. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31998664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sialic acid catabolism drives intestinal inflammation and microbial dysbiosis in mice.Nat Commun. 2015 Aug 25;6:8141. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9141. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26303108 Free PMC article.
-
Host Sialic Acids: A Delicacy for the Pathogen with Discerning Taste.Microbiol Spectr. 2015 Aug;3(4):10.1128/microbiolspec.MBP-0005-2014. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.MBP-0005-2014. Microbiol Spectr. 2015. PMID: 26350327 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akimoto, S., T. Ono, H. Tsutsui, T. Kinouchi, K. Kataoka, and Y. Ohnishi. 1994. Complete sequence of the Bacteroides fragilis Ych46 neuraminidase encoding gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 203914-921. - PubMed
-
- Angata, T., and A. Varki. 2002. Chemical diversity in the sialic acids and related α-keto acids: an evolutionary perspective. Chem. Rev. 102439-469. - PubMed
-
- Bickel, M., and G. Cimasoni. 1985. The pH of human crevicular fluid measured by a new microanalytical technique. J. Periodont. Res. 2035-40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

