Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway by olanzapine is necessary for desensitization of serotonin2A receptor-stimulated phospholipase C signaling in rat frontal cortex but not serotonin2A receptor-stimulated hormone release
- PMID: 19304867
- PMCID: PMC2888994
- DOI: 10.1177/0269881109103090
Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway by olanzapine is necessary for desensitization of serotonin2A receptor-stimulated phospholipase C signaling in rat frontal cortex but not serotonin2A receptor-stimulated hormone release
Abstract
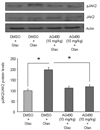
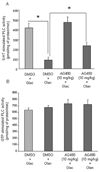
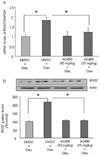
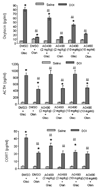
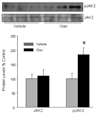
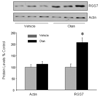
Chronic treatment with olanzapine causes desensitization of serotonin 2A receptor signaling. The purpose of the current study was to further understand the mechanisms underlying this desensitization response of serotonin 2A receptor signaling in vivo. We report that desensitization of serotonin 2A receptor stimulated-phospholipase C activity in rat frontal cortex induced by olanzapine is dependent on the activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. Olanzapine treatment for 7 days significantly increased the levels of the regulator of G protein signaling (RGS7) protein, RGS7 mRNA levels, and activation of JAK2 in rat frontal cortex. Pre-treatment with a JAK2 inhibitor AG490, significantly attenuated the olanzapine-induced reductions in serotonin 2A receptor-stimulated phospholipase C activity and prevented the olanzapine-induced increases in RGS7 mRNA and protein levels. In contrast, inhibition of the JAK-STAT pathway with AG490 did not reverse the olanzapine-induced desensitization of the serotonin 2A receptor pathway in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus mediating increases in plasma hormone levels. AG490 dose-dependently inhibited serotonin 2A receptor-stimulated oxytocin and corticosterone release. These results suggest that the olanzapine-induced increase in RGS7 expression is mediated by the activation of JAK-STAT and is necessary for olanzapine-induced desensitization of serotonin 2A receptor-stimulated phospholipase C activity in the frontal cortex but not serotonin 2A receptor-stimulated hormone release.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of the JAK-STAT pathway is necessary for desensitization of 5-HT2A receptor-stimulated phospholipase C signalling by olanzapine, clozapine and MDL 100907.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009 Jun;12(5):651-65. doi: 10.1017/S1461145708009590. Epub 2008 Oct 31. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18976543 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic olanzapine activates the Stat3 signal transduction pathway and alters expression of components of the 5-HT2A receptor signaling system in rat frontal cortex.Neuropharmacology. 2007 Sep;53(4):552-62. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2007.06.019. Epub 2007 Jul 1. Neuropharmacology. 2007. PMID: 17675105 Free PMC article.
-
Olanzapine increases RGS7 protein expression via stimulation of the Janus tyrosine kinase-signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling cascade.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007 Jul;322(1):133-40. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.120386. Epub 2007 Mar 28. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007. PMID: 17392403
-
Agonist-induced serotonin 2A receptor desensitization in the rat frontal cortex and hypothalamus.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004 Jun;309(3):1043-50. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.062067. Epub 2004 Feb 19. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2004. PMID: 14976228
-
Chronic fluoxetine differentially affects 5-hydroxytryptamine (2A) receptor signaling in frontal cortex, oxytocin- and corticotropin-releasing factor-containing neurons in rat paraventricular nucleus.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003 Aug;306(2):563-71. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.050534. Epub 2003 Apr 29. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003. PMID: 12721328
Cited by
-
G-protein receptor kinase 5 regulates the cannabinoid receptor 2-induced up-regulation of serotonin 2A receptors.J Biol Chem. 2013 May 31;288(22):15712-24. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.454843. Epub 2013 Apr 16. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23592773 Free PMC article.
-
Role of JAK-STAT and PPAR-Gamma Signalling Modulators in the Prevention of Autism and Neurological Dysfunctions.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Jun;59(6):3888-3912. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02819-1. Epub 2022 Apr 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35437700 Review.
-
JAK-STAT signaling in inflammation and stress-related diseases: implications for therapeutic interventions.Mol Biomed. 2023 Nov 8;4(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s43556-023-00151-1. Mol Biomed. 2023. PMID: 37938494 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olanzapine/Samidorphan: A New Option for the Treatment of Adults With Schizophrenia or Bipolar I Disorder.J Pharm Technol. 2022 Oct;38(5):304-313. doi: 10.1177/87551225221114281. Epub 2022 Jul 29. J Pharm Technol. 2022. PMID: 36046346 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological Properties of Chromobacterium violaceum Violacein at the Human Serotonin 2C Receptor.EC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019 Jan 29;30(Suppl 1):103-111. Epub 2016 Apr 1. EC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 33870334 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arranz MJ, Collier DA, Munro J, Sham P, Kirov G, Sodhi M, Roberts G, Price J, Kerwin RW. Analysis of a structural polymorphism in the 5-HT2A receptor and clinical response to clozapine. Neurosci Lett. 1996;217:177–178. - PubMed
-
- Banes AK, Shaw SM, Tawfik A, Patel BP, Ogbi S, Fulton D, Marrero MB. Activation of the JAK/STAT pathway in vascular smooth muscle by serotonin. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;288:C805–C812. - PubMed
-
- Benzing T, Kottgen M, Johnson M, Schermer B, Zentgraf H, Walz G, Kim E. Interaction of 14–3–3 protein with regulator of G protein signaling 7 is dynamically regulated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:32954–32962. - PubMed
-
- Benzing T, Yaffe MB, Arnould T, Sellin L, Schermer B, Schilling B, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K, Leparc GG, Kim E, Walz G. 14–3–3 interacts with regulator of G protein signaling proteins and modulates their activity. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:28167–28172. - PubMed
-
- Blackshear MA, Sanders-Bush E. Serotonin receptor sensitivity after acute and chronic treatment with mianserin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982;221:303–308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

