Antioxidant activity and phenolic content of Paederia foetida and Syzygium aqueum
- PMID: 19305354
- PMCID: PMC6253778
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules14030970
Antioxidant activity and phenolic content of Paederia foetida and Syzygium aqueum
Abstract
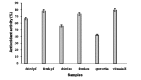
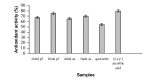
The antioxidant activity of fresh and dried plant extracts of Paederia foetida and Syzygium aqueum were studied using beta-carotene bleaching and the 2,2'-azinobis(3-ethyl-benzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) radical cation assay. The percentage of antioxidant activity for all extract samples using both assays was between 58 and 80%. The fresh samples of both plants had higher antioxidant activity than the dried samples. The results of the beta-carotene bleaching assay were correlated (R(2) = 0.9849) with those of the ABTS assay.
Figures


References
-
- Andlauer W., Fürst P. Antioxidative power of phytochemicals with special reference to cereals. Cereal Foods World. 1998;43:356–60.
-
- Amin I., Tan S.H. Antioxidant activity of selected commercial seaweeds. Malays. J. Nutr. 2002;8:167–177. - PubMed
-
- Ochse J.J., van den Brick R.C.B. Vegetables of the Dutch East Indies. A.Asher & Co; Amsterdam, The Netherland: 1977.
-
- Ghani A. Medicinal Plants of Bangladesh-Chemical Constituents and Uses. 2nd Ed. Asiatic Society of Bangladesh; Dhaka, Bangladesh: 1998.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

