Sinomenine influences capacity for invasion and migration in activated human monocytic THP-1 cells by inhibiting the expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, and CD147
- PMID: 19305422
- PMCID: PMC4002274
- DOI: 10.1038/aps.2009.21
Sinomenine influences capacity for invasion and migration in activated human monocytic THP-1 cells by inhibiting the expression of MMP-2, MMP-9, and CD147
Abstract
Aim: The aim of this study was to investigate the mechanism of the effects of Sinomenine (SIN) on the invasion and migration ability of activated human monocytic THP-1 cells (A-THP-1). Sinomenine is a pure alkaloid extracted from the Chinese medical plant Sinomenium acutum.
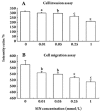
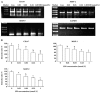
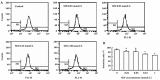
Methods: Human monocytic THP-1 cells were induced to differentiate into macrophages with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). Cells were treated with different concentrations of SIN. The invasion and migration ability of cells was tested by in vitro transwell assays. The levels of CD147 and MMPs were evaluated by flow cytometric analysis and zymographic analysis, respectively. The mRNA expression of CD147, MMP-2, and MMP-9 was measured by RT-PCR.
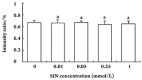
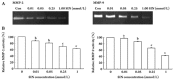
Results: The invasion and migration ability of A-THP-1 cells was significantly inhibited by SIN in a concentration-dependent fashion; at the same time, the levels of CD147, MMP-2, and MMP-9 were markedly down-regulated. This inhibitory effect was most notable at concentrations of 0.25 mmol/L and 1.00 mmol/L (P<0.01).
Conclusion: A possible mechanism of the inhibitory effect of SIN on cell invasion and migration ability is repression of the expression of MMP-2 and MMP-9, which strongly correlates with the inhibition of CD147 activity.
Figures
References
-
- Zhou H, Wong YF, Wang J, Cai X, Liu L. Sinomenine ameliorates arthritis via MMPs, TIMPs, and cytokines in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2008;376:352–7. - PubMed
-
- Hua H, Chen X.Mechanistic study of sinomenine on analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions J Xi-an Med Univ 19894346–9.Chinese.
-
- Liu L, Buchner E, Beitze D, Schmidt-Weber CB, Kaever V, Emmrich F, et al. Amelioration of rat experimental arthritides by treatment with the alkaloid sinomenine. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1996;18:529–43. - PubMed
-
- Li L, Zhang CL, Song BW.Research of the pharmacological effect of sinomenine and clinical application Tradit Chin Drug Res Clin Pharmacol 2006717–4.Chinese.
-
- Li XJ, Yue PY, Ha WY, Wong DY, Tin MM, Wang PX, et al. Effect of sinomenine on gene expression of the IL-1β-activated human synovial sarcoma. Life Sci. 2006;79:665–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

