Allosteric modulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
- PMID: 19305798
- PMCID: PMC2656816
- DOI: 10.2174/157015907781695946
Allosteric modulation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
Abstract
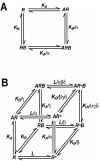
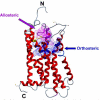
Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChRs) are prototypical Family A G protein coupled-receptors. The five mAChR subtypes are widespread throughout the periphery and the central nervous system and, accordingly, are widely involved in a variety of both physiological and pathophysiological processes. There currently remains an unmet need for better therapeutic agents that can selectively target a given mAChR subtype to the relative exclusion of others. The main reason for the lack of such selective mAChR ligands is the high sequence homology within the acetylcholine-binding site (orthosteric site) across all mAChRs. However, the mAChRs possess at least one, and likely two, extracellular allosteric binding sites that can recognize small molecule allosteric modulators to regulate the binding and function of orthosteric ligands. Extensive studies of prototypical mAChR modulators, such as gallamine and alcuronium, have provided strong pharmacological evidence, and associated structure-activity relationships (SAR), for a "common" allosteric site on all five mAChRs. These studies are also supported by mutagenesis experiments implicating the second extracellular loop and the interface between the third extracellular loop and the top of transmembrane domain 7 as contributing to the common allosteric site. Other studies are also delineating the pharmacology of a second allosteric site, recognized by compounds such as staurosporine. In addition, allosteric agonists, such as McN-A-343, AC-42 and N-desmethylclozapine, have also been identified. Current challenges to the field include the ability to effectively detect and validate allosteric mechanisms, and to quantify allosteric effects on binding affinity and signaling efficacy to inform allosteric modulator SAR.
Keywords: Acetylcholine; G protein-coupled receptor; allosteric interaction; molecular modeling; muscarinic acetylcholine receptor; mutagenesis; radioligand binding; structure-activity studies; ternary complex model..
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structure-function studies of allosteric agonism at M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors.Mol Pharmacol. 2007 Aug;72(2):463-76. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.037630. Epub 2007 May 24. Mol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17525129
-
Structural determinants of allosteric agonism and modulation at the M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor: identification of ligand-specific and global activation mechanisms.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jun 18;285(25):19012-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.125096. Epub 2010 Apr 20. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20406819 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of orthosteric and allosteric site mutations in M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors that contribute to ligand-selective signaling bias.J Biol Chem. 2010 Mar 5;285(10):7459-74. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.094011. Epub 2010 Jan 5. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20051519 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand bias at the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor family: Opportunities and challenges.Neuropharmacology. 2024 Nov 1;258:110092. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2024.110092. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Neuropharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39067666 Review.
-
Allosteric interactions at muscarinic cholinoceptors.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1998 Mar-Apr;25(3-4):185-94. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.1998.t01-4-.x. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9590567 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of residue-to-residue contact between a peptide ligand and its G protein-coupled receptor using periodate-mediated dihydroxyphenylalanine cross-linking and mass spectrometry.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 10;285(50):39425-36. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.149500. Epub 2010 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20923758 Free PMC article.
-
Structure of the human M2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor bound to an antagonist.Nature. 2012 Jan 25;482(7386):547-51. doi: 10.1038/nature10753. Nature. 2012. PMID: 22278061 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric modulators of M1 muscarinic receptors enhance acetylcholine efficacy and decrease locomotor activity and turning behaviors in zebrafish.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 28;14(1):14901. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-65445-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38942828 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of action and in vivo validation of an M4 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor allosteric modulator with potential antipsychotic properties.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010 Mar;35(4):855-69. doi: 10.1038/npp.2009.194. Epub 2009 Nov 25. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2010. PMID: 19940843 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of M1 and M4 muscarinic receptors as potential treatments for Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014 Jan 28;10:183-91. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S55104. eCollection 2014. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014. PMID: 24511233 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Andersen MB, Fink-Jensen A, Peacock L, Gerlach J, Bymaster F, Lundbaek JA, Werge T. The muscarinic M1/M4 receptor agonist xanomeline exhibits antipsychotic-like activity in Cebus apella monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2003;28:1168–1175. - PubMed
-
- Avlani V, May LT, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A. Application of a kinetic model to the apparently complex behavior of negative and positive allosteric modulators of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004;308:1062–1072. - PubMed
-
- Birdsall NJ, Farries T, Gharagozloo P, Kobayashi S, Lazareno S, Sugimoto M. Subtype-selective positive cooperative interactions between brucine analogs and acetylcholine at muscarinic receptors: functional studies. Mol. Pharmacol. 1999;55:778–786. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
