ENaC, renal sodium excretion and extracellular ATP
- PMID: 19306075
- PMCID: PMC2776138
- DOI: 10.1007/s11302-009-9150-6
ENaC, renal sodium excretion and extracellular ATP
Abstract
Sodium balance determines the extracellular fluid volume and sets arterial blood pressure (BP). Chronically raised BP (hypertension) represents a major health risk in Western societies. The relationship between BP and renal sodium excretion (the pressure/natriuresis relationship) represents the key element in defining the BP homeostatic set point. The renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) makes major adjustments to the rates of renal sodium secretion, but this system works slowly over a period of hours to days. More rapid adjustments can be made by the sympathetic nervous system, although the kidney can function well without sympathetic nerves. Attention has now focussed on regulatory mechanisms within the kidney, including extracellular nucleotides and the P2 receptor system. Here, we discuss how extracellular ATP can control renal sodium excretion by altering the activity of epithelial sodium channels (ENaC) present in the apical membrane of principal cells. There remains considerable controversy over the molecular targets for released ATP, although the P2Y(2) receptor has received much attention. We review the available data and reflect on our own findings in which ATP-activated P2Y and P2X receptors make adjustments to ENaC activity and therefore sodium excretion.
Figures
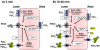
Similar articles
-
Regulation of renal NaCl and water transport by the ATP/UTP/P2Y2 receptor system.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):F463-75. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00236.2011. Epub 2011 Jun 29. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21715471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Na+ excretion and arterial blood pressure by purinergic signalling intrinsic to the distal nephron: consequences and mechanisms.Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2015 Jan;213(1):213-21. doi: 10.1111/apha.12372. Epub 2014 Sep 12. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 2015. PMID: 25154328 Review.
-
Compensatory up-regulation of angiotensin II subtype 1 receptors in alpha ENaC knockout heterozygous mice.Kidney Int. 2001 Jun;59(6):2216-21. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00739.x. Kidney Int. 2001. PMID: 11380824
-
Collecting duct prorenin receptor knockout reduces renal function, increases sodium excretion, and mitigates renal responses in ANG II-induced hypertensive mice.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017 Dec 1;313(6):F1243-F1253. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00152.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28814438 Free PMC article.
-
Intrinsic control of sodium excretion in the distal nephron by inhibitory purinergic regulation of the epithelial Na(+) channel.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012 Jan;21(1):52-60. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0b013e32834db4a0. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 22143248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Deletion of P2Y2 Receptor Offers Long-Term (5 Months) Protection Against Lithium-Induced Polyuria, Natriuresis, Kaliuresis, and Collecting Duct Remodeling and Cell Proliferation.Front Physiol. 2018 Dec 17;9:1765. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2018.01765. eCollection 2018. Front Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30618788 Free PMC article.
-
Salt-deficient diet exacerbates cystogenesis in ARPKD via epithelial sodium channel (ENaC).EBioMedicine. 2019 Feb;40:663-674. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.006. Epub 2019 Feb 8. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30745171 Free PMC article.
-
Introduction and perspective, historical note.Front Cell Neurosci. 2013 Nov 21;7:227. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00227. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24312014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purinergic signalling in the kidney in health and disease.Purinergic Signal. 2014 Mar;10(1):71-101. doi: 10.1007/s11302-013-9400-5. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Purinergic Signal. 2014. PMID: 24265071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P2X Receptors Inhibit NaCl Absorption in mTAL Independently of Nitric Oxide.Front Physiol. 2017 Jan 24;8:18. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00018. eCollection 2017. Front Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28174542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1172/JCI2729', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1172/jci2729'}, {'type': 'PMC', 'value': 'PMC509060', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC509060/'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '9649552', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9649552/'}]}
- Mall M, Bleich M, Greger R, Schreiber R, Kunzelmann K (1998) The amiloride-inhibitable Na+ conductance is reduced by the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator in normal but not in cystic fibrosis airways. J Clin Invest 102:15–21 - PMC - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '16410345', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16410345/'}]}
- Kunzelmann K, Scheidt K, Scharf B, Ousingsawat J, Schreiber R, Wainwright B, McMorran B (2006) Flagellin of Pseudomonas aeruginosa inhibits Na+ transport in airway epithelia. FASAB J 20:545–546 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '11880338', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11880338/'}]}
- Schwiebert EM, Wallace DP, Braunstein GM, King SR, Peti-Peterdi J, Hanaoka K, Guggino WB, Guay-Woodford LM, Bell PD, Sullivan LP, Grantham JJ, Taylor AL (2002) Autocrine extracellular purinergic signalling in epithelial cells derived from polycystic kidneys. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 282(4):F763–F775 - PubMed
-
- {'text': '', 'ref_index': 1, 'ids': [{'type': 'DOI', 'value': '10.1126/science.2063193', 'is_inner': False, 'url': 'https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2063193'}, {'type': 'PubMed', 'value': '2063193', 'is_inner': True, 'url': 'https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/2063193/'}]}
- Guyton AC (1991) Blood pressure control—special role of the kidneys and body fluids. Science 252:1813–1816 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

