Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and the blood-brain barrier
- PMID: 19306229
- PMCID: PMC2744422
- DOI: 10.1080/13550280902769764
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and the blood-brain barrier
Abstract
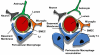
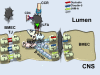
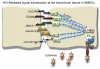
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) plays a critical role in normal physiology of the central nervous system by regulating what reaches the brain from the periphery. The BBB also plays a major role in neurologic disease including neuropathologic sequelae associated with infection by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in humans and the closely related simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) in macaques. In this review, we provide an overview of the function, structure, and components of the BBB, followed by a more detailed discussion of the subcellular structures and regulation of the tight junction. We then discuss the ways in which HIV/SIV affects the BBB, largely through infection of monocytes/macrophages, and how infected macrophages crossing the BBB ultimately results in breakdown of the barrier.
Figures


References
-
- Agrawal L, Louboutin JP, Strayer DS. Preventing HIV-1 Tat-induced neuronal apoptosis using antioxidant enzymes: mechanistic and therapeutic implications. Virology. 2007;363:462–72. - PubMed
-
- Andras IE, Pu H, Deli MA, Nath A, Hennig B, Toborek M. HIV-1 Tat protein alters tight junction protein expression and distribution in cultured brain endothelial cells. J Neurosci Res. 2003;74:255–65. - PubMed
-
- Andras IE, Pu H, Tian J, Deli MA, Nath A, Hennig B, Toborek M. Signaling mechanisms of HIV-1 Tat-induced alterations of claudin-5 expression in brain endothelial cells. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2005;25:1159–70. - PubMed
-
- Annunziata P. Blood-brain barrier changes during invasion of the central nervous system by HIV-1. Old and new insights into the mechanism. J Neurol. 2003;250:901–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

