Endothelium-dependent vasodilatation and exercise hyperaemia in ageing humans: impact of acute ascorbic acid administration
- PMID: 19307300
- PMCID: PMC2689338
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2008.167320
Endothelium-dependent vasodilatation and exercise hyperaemia in ageing humans: impact of acute ascorbic acid administration
Abstract
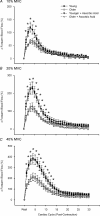
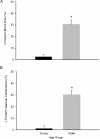
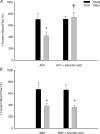
Age-related increases in oxidative stress impair endothelium-dependent vasodilatation in humans, leading to the speculation that endothelial dysfunction contributes to impaired muscle blood flow and vascular control during exercise in older adults. We directly tested this hypothesis in 14 young (22 +/- 1 years) and 14 healthy older men and women (65 +/- 2 years). We measured forearm blood flow (FBF; Doppler ultrasound) and calculated vascular conductance (FVC) responses to single muscle contractions at 10, 20 and 40% maximum voluntary contraction (MVC) before and during ascorbic acid (AA) infusion, and we also determined the effects of AA on muscle blood flow during mild (10% MVC) continuous rhythmic handgrip exercise. For single contractions, the peak rapid hyperaemic responses to all contraction intensities were impaired approximately 45% in the older adults (all P < 0.05), and AA infusion did not impact the responses in either age group. For the rhythmic exercise trial, FBF (approximately 28%) and FVC (approximately 31%) were lower (P = 0.06 and 0.05) in older versus young adults after 5 min of steady-state exercise with saline. Subsequently, AA was infused via brachial artery catheter for 10 min during continued exercise. AA administration did not significantly influence FBF or FVC in young adults (1-3%; P = 0.24-0.59), whereas FBF increased 34 +/- 7% in older adults at end-exercise, and this was due to an increase in FVC (32 +/- 7%; both P < 0.05). This increase in FBF and FVC during exercise in older adults was associated with improvements in vasodilator responses to acetylcholine (ACh; endothelium dependent) but not sodium nitroprusside (SNP; endothelium independent). AA had no effect on ACh or SNP responses in the young. We conclude that acute AA administration does not impact the observed age-related impairment in the rapid hyperaemic response to brief muscle contractions in humans; however, it does significantly increase muscle blood flow during continuous dynamic exercise in older adults, and this is probably due (in part) to an improvement in endothelium-dependent vasodilatation.
Figures



Comment in
-
Keeping the juices flowing with age: vitamin C and exercise hyperaemia.J Physiol. 2009 Jun 1;587(Pt 11):2423. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.173633. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19483250 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Bailey DM, Lawrenson L, McEnemy J, Young IS, James PE, Jackson SK, Henry RR, Mathieu-Costello O, McCord JM, Richardson RS. Electron paramagnetic spectroscopic evidence of exercise-induced free radical accumulation in human skeletal muscle. Free Rad Res. 2007;41:182–190. - PubMed
-
- Bohm F, Settergren M, Pernow J. Vitamin C blocks vascular dysfunction and release of interleukin-6 induced by endothelin-1 in humans in vivo. Atherosclerosis. 2007;190:408–415. - PubMed
-
- Brock RW, Tschakovsky ME, Shoemaker JK, Halliwill JR, Joyner MJ, Hughson RL. Effects of acetylcholine and nitric oxide on forearm blood flow at rest and after a single contraction. J Appl Physiol. 1998;85:2249–2254. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

