The RNA-binding protein Elavl1/HuR is essential for placental branching morphogenesis and embryonic development
- PMID: 19307312
- PMCID: PMC2682039
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.01393-08
The RNA-binding protein Elavl1/HuR is essential for placental branching morphogenesis and embryonic development
Abstract
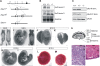
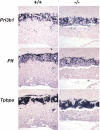
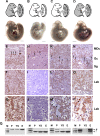
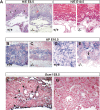
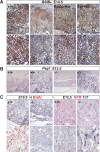
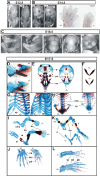
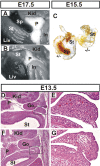
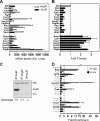
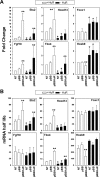
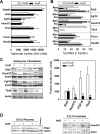
HuR is an RNA-binding protein implicated in a diverse array of pathophysiological processes due to its effects on the posttranscriptional regulation of AU- and U-rich mRNAs. Here we reveal HuR's requirement in embryonic development through its genetic ablation. Obligatory HuR-null embryos exhibited a stage retardation phenotype and failed to survive beyond midgestation. By means of conditional transgenesis, we restricted HuR's mutation in either embryonic or endothelial compartments to demonstrate that embryonic lethality is consequent to defects in extraembryonic placenta. HuR's absence impaired the invagination of allantoic capillaries into the chorionic trophoblast layer and the differentiation of syncytiotrophoblast cells that control the morphogenesis and vascularization of the placental labyrinth and fetal support. HuR-null embryos rescued from these placental defects proceeded to subsequent developmental stages but displayed defects in skeletal ossification, fusions in limb elements, and asplenia. By coupling gene expression measurements, data meta-analysis, and HuR-RNA association assays, we identified transcription and growth factor mRNAs controlled by HuR, primarily at the posttranscriptional level, to guide morphogenesis, specification, and patterning. Collectively, our data demonstrate the dominant role of HuR in organizing gene expression programs guiding placental labyrinth morphogenesis, skeletal specification patterns, and splenic ontogeny.
Figures
References
-
- Abdelmohsen, K., A. Lal, H. H. Kim, and M. Gorospe. 2007. Posttranscriptional orchestration of an anti-apoptotic program by HuR. Cell Cycle 61288-1292. - PubMed
-
- Anson-Cartwright, L., K. Dawson, D. Holmyard, S. J. Fisher, R. A. Lazzarini, and J. C. Cross. 2000. The glial cells missing-1 protein is essential for branching morphogenesis in the chorioallantoic placenta. Nat. Genet. 25311-314. - PubMed
-
- Bell, S. E., M. J. Sanchez, O. Spasic-Boskovic, T. Santalucia, L. Gambardella, G. J. Burton, J. J. Murphy, J. D. Norton, A. R. Clark, and M. Turner. 2006. The RNA binding protein Zfp36l1 is required for normal vascularisation and post-transcriptionally regulates VEGF expression. Dev. Dyn. 2353144-3155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
