Identification of the efflux transporter of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic ciprofloxacin in murine macrophages: studies with ciprofloxacin-resistant cells
- PMID: 19307362
- PMCID: PMC2687251
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.01428-08
Identification of the efflux transporter of the fluoroquinolone antibiotic ciprofloxacin in murine macrophages: studies with ciprofloxacin-resistant cells
Abstract
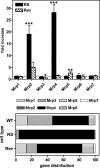
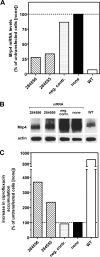
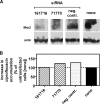
Ciprofloxacin, the most widely used totally synthetic antibiotic, is subject to active efflux mediated by a MRP-like transporter in wild-type murine J774 macrophages. To identify the transporter among the seven potential Mrps, we used cells made resistant to ciprofloxacin obtained by long-term exposure to increasing drug concentrations (these cells show less ciprofloxacin accumulation and provide a protected niche for ciprofloxacin-sensitive intracellular Listeria monocytogenes). In the present paper, we first show that ciprofloxacin-resistant cells display a faster efflux of ciprofloxacin which is inhibited by gemfibrozil (an unspecific MRP inhibitor). Elacridar, at a concentration known to inhibit P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), only slightly increased ciprofloxacin accumulation, with no difference between resistant and wild-type cells. Analysis at the mRNA (real-time PCR) and protein (Western blotting) levels revealed an overexpression of Mrp2 and Mrp4. Mrp4 transcripts, however, were overwhelmingly predominant (45% [wild-type cells] to 95% [ciprofloxacin-resistant cells] of all Mrp transcripts tested [Mrp1 to Mrp7]). Silencing of Mrp2 and Mrp4 with specific small interfering RNAs showed that only Mrp4 is involved in ciprofloxacin transport in both ciprofloxacin-resistant and wild-type cells. The study therefore identifies Mrp4 as the most likely transporter of ciprofloxacin in murine macrophages but leaves open a possible common upregulation mechanism for both Mrp4 and Mrp2 upon chronic exposure of eukaryotic cells to this widely used antibiotic.
Figures



References
-
- Almquist, K. C., D. W. Loe, D. R. Hipfner, J. E. Mackie, S. P. C. Cole, and R. G. Deeley. 1995. Characterization of the Mr 190,000 multidrug resistance protein (MRP) in drug-selected and transfected human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 55:102-110. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez, A. I., M. Perez, J. G. Prieto, A. J. Molina, R. Real, and G. Merino. 2008. Fluoroquinolone efflux mediated by ABC transporters. J. Pharm. Sci. 97:3483-3493. - PubMed
-
- Annereau, J. P., G. Szakacs, C. J. Tucker, A. Arciello, C. Cardarelli, J. Collins, S. Grissom, B. R. Zeeberg, W. Reinhold, J. N. Weinstein, Y. Pommier, R. S. Paules, and M. M. Gottesman. 2004. Analysis of ATP-binding cassette transporter expression in drug-selected cell lines by a microarray dedicated to multidrug resistance. Mol. Pharmacol. 66:1397-1405. - PubMed
-
- Anonymous. 2003. Whither RNAi? Nat. Cell Biol. 5:489-490. - PubMed
-
- Baran, Y., B. Gur, P. Kaya, A. U. Ural, F. Avcu, and U. Gunduz. 2007. Upregulation of multi drug resistance genes in doxorubicin resistant human acute myelogeneous leukemia cells and reversal of the resistance. Hematology 12:511-517. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

