Social isolation alters neuroinflammatory response to stroke
- PMID: 19307557
- PMCID: PMC2667090
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0810737106
Social isolation alters neuroinflammatory response to stroke
Abstract
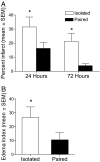
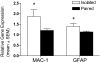
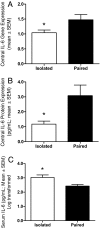
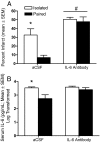
Social isolation has dramatic long-term physiological and psychological consequences; however, the mechanisms by which social isolation influences disease outcome are largely unknown. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the effects of social isolation on neuronal damage, neuroinflammation, and functional outcome after focal cerebral ischemia. Male mice were socially isolated (housed individually) or pair housed with an ovariectomized female before induction of stroke, via transient intraluminal middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), or SHAM surgery. In these experiments, peri-ischemic social isolation decreases poststroke survival rate and exacerbates infarct size and edema development. The social influence on ischemic damage is accompanied by an altered neuroinflammatory response; specifically, central interleukin-6 (IL-6) signaling is down-regulated, whereas peripheral IL-6 is up-regulated, in isolated relative to socially housed mice. In addition, intracerebroventricular injection of an IL-6 neutralizing antibody (10 ng) eliminates social housing differences in measures of ischemic outcome. Taken together, these data suggest that central IL-6 is an important mediator of social influences on stroke outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Boden-Albala B, Litwak E, Elkind MS, Rundek T, Sacco RL. Social isolation and outcomes post stroke. Neurology. 2005;64:1888–1892. - PubMed
-
- Lett HS, et al. Social support and prognosis in patients at increased psychosocial risk recovering from myocardial infarction. Health Psychol. 2007;26:418–427. - PubMed
-
- Barry LC, Kasl SV, Lichtman J, Vaccarino V, Krumholz HM. Social support and change in health-related quality of life 6 months after coronary artery bypass grafting. J Psychosom Res. 2006;60:185–193. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda A, et al. Social support and stroke and coronary heart disease: The JPHC study cohorts II. Stroke. 2008;39:768–775. - PubMed
-
- Cohen S, Lemay EP. Why would social networks be linked to affect and health practices? Health Psychol. 2007;26:410–417. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

