LL-37 inhibits serum amyloid A-induced IL-8 production in human neutrophils
- PMID: 19307752
- PMCID: PMC2701981
- DOI: 10.3858/emm.2009.41.5.036
LL-37 inhibits serum amyloid A-induced IL-8 production in human neutrophils
Abstract
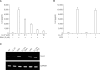
Serum amyloid A (SAA) has been regarded as an important mediator of inflammatory responses. The effect of several formyl peptide receptor-like 1 (FPRL1) ligands on the production of IL-8 by SAA was investigated in human neutrophils. Among the ligands tested, LL-37 was found to specifically inhibit SAA-induced IL-8 production in transcriptional and post-transcriptional levels. Since SAA stimulated IL-8 production via ERK and p38 MAPK in human neutrophils, we tested the effect of LL-37 on SAA induction for these two MAPKs. LL-37 caused a dramatic inhibition of ERK and p38 MAPK activity, which is induced by SAA. LL-37 was also found to inhibit SAA-stimulated neutrophil chemotactic migration. Further, the LL-37-induced inhibitory effect was mediated by FPRL1. Our findings indicate that LL-37 is expected to be useful in the inhibition of SAA signaling and for the development of drugs against SAA-related inflammatory diseases.
Figures
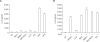
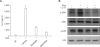
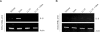
Similar articles
-
Acute-serum amyloid A and A-SAA-derived peptides as formyl peptide receptor (FPR) 2 ligands.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 3;14:1119227. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1119227. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36817589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum amyloid A induces IL-8 secretion through a G protein-coupled receptor, FPRL1/LXA4R.Blood. 2003 Feb 15;101(4):1572-81. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-05-1431. Epub 2002 Sep 26. Blood. 2003. PMID: 12393391
-
Lysophosphatidylglycerol inhibits formyl peptide receptorlike-1-stimulated chemotactic migration and IL-1beta production from human phagocytes.Exp Mol Med. 2009 Aug 31;41(8):584-91. doi: 10.3858/emm.2009.41.8.064. Exp Mol Med. 2009. PMID: 19381066 Free PMC article.
-
An antimicrobial cathelicidin peptide, human CAP18/LL-37, suppresses neutrophil apoptosis via the activation of formyl-peptide receptor-like 1 and P2X7.J Immunol. 2006 Mar 1;176(5):3044-52. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.176.5.3044. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16493063
-
Opposing regulation of neutrophil apoptosis through the formyl peptide receptor-like 1/lipoxin A4 receptor: implications for resolution of inflammation.J Leukoc Biol. 2008 Sep;84(3):600-6. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1107765. Epub 2008 May 21. J Leukoc Biol. 2008. PMID: 18495783 Review.
Cited by
-
Formylpeptide receptor 2: Nomenclature, structure, signalling and translational perspectives: IUPHAR review 35.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Oct;179(19):4617-4639. doi: 10.1111/bph.15919. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35797341 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute-serum amyloid A and A-SAA-derived peptides as formyl peptide receptor (FPR) 2 ligands.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Feb 3;14:1119227. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1119227. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36817589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Formyl Peptide Receptors: Diversity of Ligands and Mechanism for Recognition.Molecules. 2017 Mar 13;22(3):455. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030455. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28335409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct signaling cascades elicited by different formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2) agonists.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Apr 2;14(4):7193-230. doi: 10.3390/ijms14047193. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23549262 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cathelicidin impact on inflammatory cells.Cent Eur J Immunol. 2015;40(2):225-35. doi: 10.5114/ceji.2015.51359. Epub 2015 Aug 3. Cent Eur J Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26557038 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bae YS, Bae H, Kim Y, Lee TG, Suh PG, Ryu SH. Identification of novel chemoattractant peptides for human leukocytes. Blood. 2001;97:2854–2862. - PubMed
-
- Bae YS, Yi HJ, Lee HY, Jo EJ, Kim JI, Lee TG, Ye RD, Kwak JY, Ryu SH. Differential activation of formyl peptide receptor-like 1 by peptide ligands. J Immunol. 2003;71:6807–6813. - PubMed
-
- Coxon PY, Rane MJ, Uriarte S, Powell DW, Singh S, Butt W, Chen Q, McLeish KR. MAPK-activated protein kinase-2 participates in p38 MAPK-dependent and ERK-dependent functions in human neutrophils. Cell Signal. 2003;15:993–1001. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
